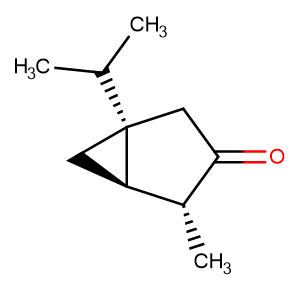
Thujone
CAS No. 546-80-5
Thujone( ALPHA-(-)-THUJONE )
Catalog No. M21289 CAS No. 546-80-5
Thujone is an inhibitor of ?ACh with an IC50 value of 24.7μM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 110 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameThujone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThujone is an inhibitor of ?ACh with an IC50 value of 24.7μM.
-
DescriptionThujone is an inhibitor of ?ACh with an IC50 value of 24.7μM.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsALPHA-(-)-THUJONE
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorGABAA|AChR
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number546-80-5
-
Formula Weight152.23
-
Molecular FormulaC10H16O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (656.90 mM)
-
SMILESCC(C)[C@](C1)(C2)[C@H]1[C@@H](C)C2=O
-
Chemical Name1-Isopropyl-4-methylbicyclo(3.1.0)hexan-3-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Biatractylolide
Biatractylolide has a neuroprotective effect on glutamate-induced injury in PC12 and SH-SY5Y cells through a mechanism of the PI3K-Akt-GSK3β-dependent pathways.
-
TCS 1105
TCS 1105 is a GABAA benzodiazepine receptor (BZR) ligand. TCS 1105 blocks Sema3A induced axonal growth cones collapse. TCS 1105 reduces anxiety-like behavior and enhances offensive behavior and social dominance in mice.
-
(Arg)9 TFA
(Arg)9 TFA (Nona-L-arginine TFA), a cell-penetrating peptide, exhibits neuroprotective activity with an IC50 of 0.78 μM in the glutamic acid model.Poly-arginine (e.g. (Arg)9) and arginine-rich peptides (e.g. TAT, penetratin), which belong to a class of peptides with cell-penetrating properties are neuroprotective.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


