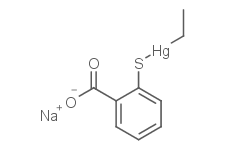
Thimerosal
CAS No. 54-64-8
Thimerosal( Thiomersalate | Mercurothiolate )
Catalog No. M19490 CAS No. 54-64-8
Thimerosal is an organomercurial compound and derivative of thiosalicyclic acid with antibacterial and antifungal properties.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameThimerosal
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThimerosal is an organomercurial compound and derivative of thiosalicyclic acid with antibacterial and antifungal properties.
-
DescriptionThimerosal is an organomercurial compound and derivative of thiosalicyclic acid with antibacterial and antifungal properties. Although the mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated thimerosal inhibits sulfhydryl-containing active site of various enzymes and binds to sulfhydryl compounds such as glutathione cysteine and SH groups of proteins. In addition thimerosal activates the InsP3 calcium channel on endoplasmic reticular membrane thereby triggering the release of calcium from intracellular stores resulting in a calcium-induced calcium-influx of extracellular calcium. Consequently thimerosal may induce or inhibit cellular functions dependent on calcium signaling.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoThe Thimerosal (THIM) administration increases μ-opioid receptors (MORs) density in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with higher doses of Thimerosal statistically significantly increases MOR density in the dorsomedial periaqueductal gray (DMPAG) andlateral periaqueductal gray (LPAG) regions. At the dose 3,000 μg Hg/kg, Thimerosal also augments MOR density in the caudate putamen (CPU). In contrast, the administration of Thimerosal at both higher doses decreases MOR density in the dentate gyrus (DG). Thimerosal administration (4 injections, i.m., 240 μg Hg/kg on postnatal days 7, 9, 11, 15) induces lasting changes in amino acid overflow: an increase of glutamate and aspartate accompanied by a decrease of glycine and alanine; measured 10 to 14 weeks after the injections. Four injections of Thimerosal at a dose of 12.5 μg Hg/kg do not alter glutamate and aspartate concentrations at microdialysis time. Application of Thimerosal to the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in perfusion fluid evokes a rapid increase of glutamate overflow. Coadministration of the neurosteroid, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS; 80 mg/kg; i.p.) prevents the Thimerosal effect on glutamate and aspartate; the steroid alone has no influence on these amino acids. Coapplication of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) with Thimerosal in perfusion fluid also blocks the acute action of Thimerosal on glutamate.
-
SynonymsThiomersalate | Mercurothiolate
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorAntibacterial
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
IndicationSeptic; Fungal Infection
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number54-64-8
-
Formula Weight404.81
-
Molecular FormulaC9H9HgNaO2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILES[Na+].CC[Hg]SC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Li X et al. Toxicol Sci. 2014 Jun;139(2):452-65.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Bisdionin C
Bisdionin C is a potent inhibitor of GH18 chitinase with an IC50 of 0.2 μM for A. fumigatus ChiB1. Bisdionin C inhibits human macrophage chitotriosidase(HCHT, IC50 = 8.3 μM) and acidic mammalian chitinase (AMCase, IC50 = 3.4 μM).
-
Glyceryl monocaprate
Glyceryl monocaprate has inhibitory effect on Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). It also offers an effective treatment for herpes labialiss.
-
Glycol chitosan
Glycol chitosan is a chitosan derivative with hydrophilic ethylene glycol branches.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


