Thiamphenicol
CAS No. 15318-45-3
Thiamphenicol( NSC 522822 | (+)-Thiamphenicol | Thiophenicol | WIN 5,603-2 )
Catalog No. M12153 CAS No. 15318-45-3
Thiamphenicol is an antimicrobial antibiotic and a methyl-sulfonyl analogue of chloramphenicol.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 60 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameThiamphenicol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThiamphenicol is an antimicrobial antibiotic and a methyl-sulfonyl analogue of chloramphenicol.
-
DescriptionThiamphenicol is an antimicrobial antibiotic and a methyl-sulfonyl analogue of chloramphenicol.(In Vitro):Thiamphenicol shows a significant post-antibiotic effect (PAE) (0.33 to 2.9h) on all pathogens studied (S. pneumoniae, S. aureus and Escherichia coli) and a powerful bactericidal effect against β-lactamase-positive and -negative H. influenzae. Thiamphenicol MICs for the microorganisms analyzed are: 32 mg/L (S. aureus and E. coli), 2 mg/L (S. pneumoniae) and 0.25 mg/L (H. influenzae). Thiamphenicol shows a good in vitro activity against difficult-to-treat multiply resistant pathogens.(In Vivo):The pharmacokinetics of Thiamphenicol (30 mg/kg) after single intravenous (IV) and oral (PO) administration is investigated in Mulard ducks. After IV administration, for Thiamphenicol, the mean residence time is 2.83 hours, the general half-life is 1.96 hours, the clearance is 0.04 L/hr/kg. Pharmacokinetics after PO administration is very similar for IV administration. Thiamphenicol shows rapid absorption and bioavailability of more than 70%.
-
In VitroThiamphenicol shows a significant post-antibiotic effect (PAE) (0.33 to 2.9h) on all pathogens studied (S. pneumoniae, S. aureus and Escherichia coli) and a powerful bactericidal effect against β-lactamase-positive and -negative H. influenzae. Thiamphenicol MICs for the microorganisms analyzed are: 32 mg/L (S. aureus and E. coli), 2 mg/L (S. pneumoniae) and 0.25 mg/L (H. influenzae). Thiamphenicol shows a good in vitro activity against difficult-to-treat multiply resistant pathogens.
-
In VivoThe pharmacokinetics of Thiamphenicol (30 mg/kg) after single intravenous (IV) and oral (PO) administration is investigated in Mulard ducks. After IV administration, for Thiamphenicol, the mean residence time is 2.83 hours, the general half-life is 1.96 hours, the clearance is 0.04 L/hr/kg. Pharmacokinetics after PO administration is very similar for IV administration. Thiamphenicol shows rapid absorption and bioavailability of more than 70%.
-
SynonymsNSC 522822 | (+)-Thiamphenicol | Thiophenicol | WIN 5,603-2
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number15318-45-3
-
Formula Weight356.22
-
Molecular FormulaC12H15Cl2NO5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 71 mg/mL (199.31 mM)
-
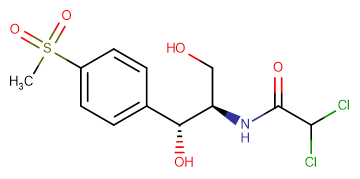
SMILESO=C(N[C@H](CO)[C@H](O)C1=CC=C(S(=O)(C)=O)C=C1)C(Cl)Cl
-
Chemical Name2,2-dichloro-N-((1R,2R)-1,3-dihydroxy-1-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)acetamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Berman HM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1; 28(1): 235-42.
molnova catalog



related products
-
HPV-E7-C
HPV-E7-C
-
ML-180
ML-180 is a potent orphan nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog 1 (LRH-1; NR5A2) inverse agonist (IC50 of 3.7 μM) .ML-180 (0.5-5 μM; 24 hours) shows a significant inhibition of cyclin-D1 and cyclin-E1 expression in hepatic cells, but has little effect on repression in SK-OV-3 cells[2]. ML-180 (5 μM; 24 hours) leads to a rapid decrease of LRH-1 expression and efficiently represses endogenous LRH-1 signaling.
-
4-CMTB
4-CMTB is a selective agonist of FFA2 and GPR43.It also is a positive allosteric modulator (pEC50=6.38).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


