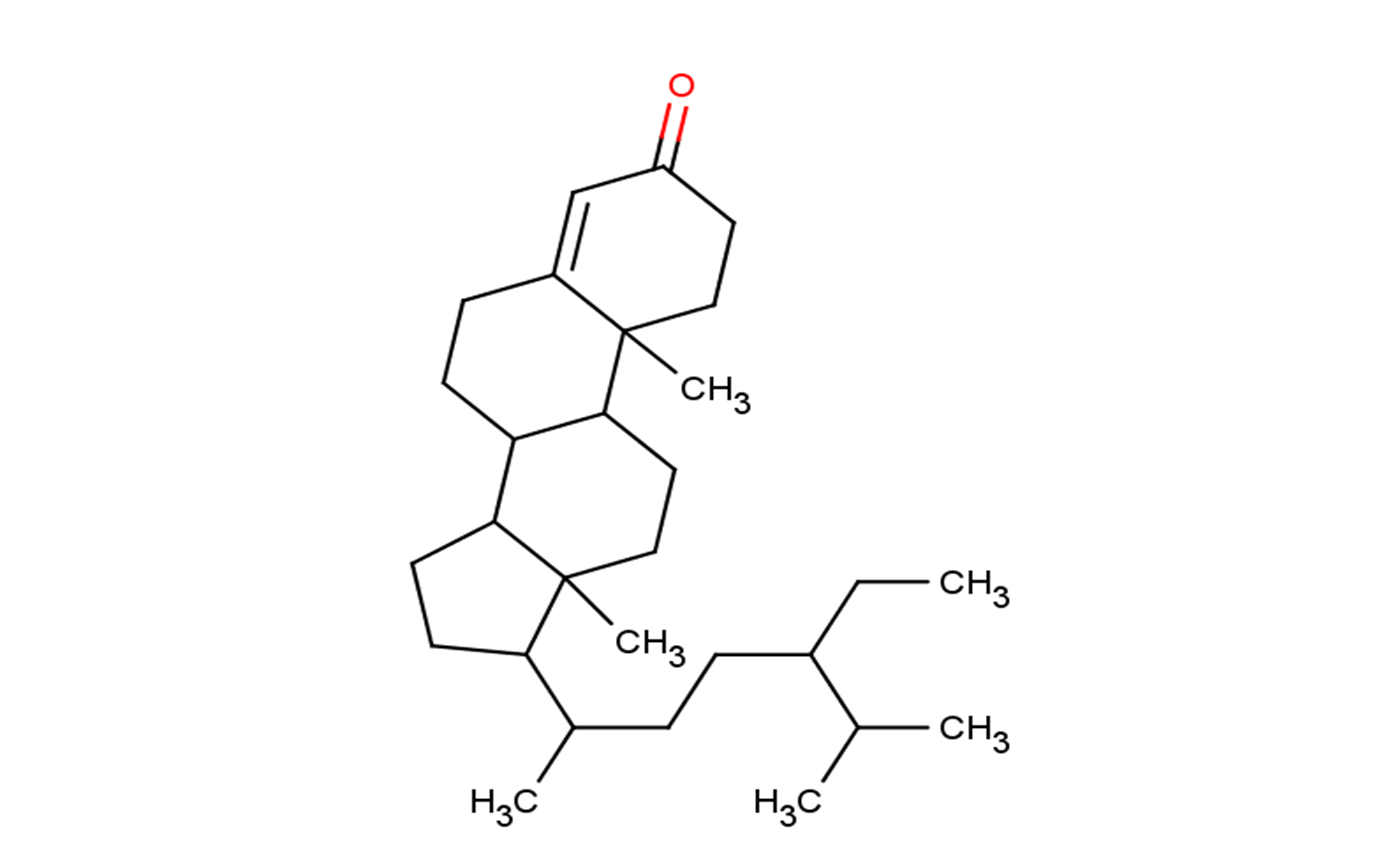
Sitostenone
CAS No. 1058-61-3
Sitostenone( —— )
Catalog No. M22863 CAS No. 1058-61-3
Sitostenone has antioxidation activity. Stigmasta-4-en-3-one(Sitostenone) can be used for the treatment of androgen-dependent diseases, especially for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 216 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 320 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 529 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 770 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1062 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSitostenone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSitostenone has antioxidation activity. Stigmasta-4-en-3-one(Sitostenone) can be used for the treatment of androgen-dependent diseases, especially for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
-
DescriptionSitostenone has antioxidation activity. Stigmasta-4-en-3-one(Sitostenone) can be used for the treatment of androgen-dependent diseases, especially for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1058-61-3
-
Formula Weight412.7
-
Molecular FormulaC29H48O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCCC(CCC(C)C1CCC2C1(CCC3C2CCC4=CC(=O)CCC34C)C)C(C)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Antioxidant and anticancer aporphine alkaloids from the leaves of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. cv. Rosa-plena. Molecules. 2014 Nov 3;19(11):17829-38
molnova catalog



related products
-
Solvent Yellow 93
Solvent Yellow 93, an azomethine dye, is used as a colorant of toner.
-
2-Amino-4-hydroxypyr...
2-Amino-4-hydroxypyrrolo[23- d]pyrimidi
-
N-Formylcytisine
N-Formylcytisine is a natural product isolated from the stem bark of Maackia amurensis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


