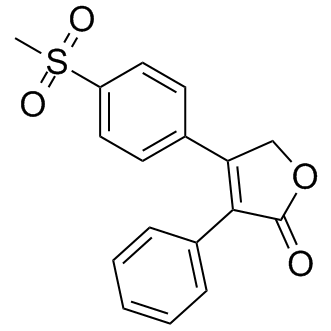
Rofecoxib
CAS No. 162011-90-7
Rofecoxib( MK-0996 | MK-966 )
Catalog No. M12377 CAS No. 162011-90-7
A potent, selective and orally active COX-2 inhibitor with IC50 of 26 nM for inhibition of the COX-2-dependent production of PGE2 in human osteosarcoma cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 56 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRofecoxib
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA potent, selective and orally active COX-2 inhibitor with IC50 of 26 nM for inhibition of the COX-2-dependent production of PGE2 in human osteosarcoma cells.
-
DescriptionA potent, selective and orally active COX-2 inhibitor with IC50 of 26 nM for inhibition of the COX-2-dependent production of PGE2 in human osteosarcoma cells; displays 1,000-fold selectivity over COX-1 activity; selectively inhibits LPS-induced, COX-2-derived PGE(2) synthesis after blood coagulation (IC50=0.53 uM); exhibits anti-inflammation activity in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis rodent models.Pain Withdrawn(In Vitro):Rofecoxib (MK-0966) is a potent and orally active inhibitor of COX-2, with IC50s of 26 and 18 nM for human COX-2 in human osteosarcoma cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells, with a 1000-fold selectivity for COX-2 over COX-1 (IC50 >50 μM in U937 cells and >15 μM in Chinese hamster ovary cells). Rofecoxib time dependently inhibits purified human recombinant COX-2 (IC50=0.34 μM) but suppresses purified human COX-1 in a non-time-dependent manner that can only be observed at a very low substrate concentration (IC50=26 μM at 0.1 μM arachidonic acid concentration). Rofecoxib selectively inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced, COX-2-derived PGE(2) synthesis with an IC50 value of 0.53 ± 0.02 μM compared with an IC50 value of 18.8 ± 0.9 μM for the inhibition of COX-1-derived thromboxane B(2) synthesis after blood coagulation. Rofecoxib (36 μM) causes a cell proliferation of 68% in MPP89, of 58% in Ist-Mes-1 and 40% in Ist-Mes-2. MSTO-211H and NCI-H2452 treated with 36 μM of Rofecoxib have a survival of 97% and 90% respectively. Rofecoxib (36 μM) decreases COX-2 and mRNA levels in Ist-Mes-1, Ist-Mes-2 and MPP89 cell lines. (In Vivo):Rofecoxib potently inhibits carrageenan-induced paw edema (ID50=1.5 mg/kg), carrageenan-induced paw hyperalgesia (ID50=1.0 mg/kg), lipopolysaccharide-induced pyresis (ID50=0.24 mg/kg), and adjuvant-induced arthritis (ID50=0.74 mg/kg/day) in rodent models. Rofecoxib also protects adjuvant-induced destruction of cartilage and bone structures in rats. In a 51Cr excretion assay for detection of gastrointestinal integrity in either rats or squirrel monkeys, rofecoxib shows no effect at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day for 5 days. Rofecoxib (15 mg/kg, i.p.) reduces the blood vessels attached to the internal limiting membrane (ILM) in mice. COX-2 and VEGF protein expressions, COX-2 mRNA and VEGF mRNA are also significantly decreased by Rofecoxib in ROP mice.
-
In VitroRofecoxib (MK-0966) is a potent and orally active inhibitor of COX-2, with IC50s of 26 and 18 nM for human COX-2 in human osteosarcoma cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells, with a 1000-fold selectivity for COX-2 over COX-1 (IC50 >50 μM in U937 cells and >15 μM in Chinese hamster ovary cells). Rofecoxib time dependently inhibits purified human recombinant COX-2 (IC50=0.34 μM) but suppresses purified human COX-1 in a non-time-dependent manner that can only be observed at a very low substrate concentration (IC50=26 μM at 0.1 μM arachidonic acid concentration). Rofecoxib selectively inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced, COX-2-derived PGE(2) synthesis with an IC50 value of 0.53 ± 0.02 μM compared with an IC50 value of 18.8 ± 0.9 μM for the inhibition of COX-1-derived thromboxane B(2) synthesis after blood coagulation. Rofecoxib (36 μM) causes a cell proliferation of 68% in MPP89, of 58% in Ist-Mes-1 and 40% in Ist-Mes-2. MSTO-211H and NCI-H2452 treated with 36 μM of Rofecoxib have a survival of 97% and 90% respectively. Rofecoxib (36 μM) decreases COX-2 and mRNA levels in Ist-Mes-1, Ist-Mes-2 and MPP89 cell lines.
-
In VivoRofecoxib potently inhibits carrageenan-induced paw edema (ID50=1.5 mg/kg), carrageenan-induced paw hyperalgesia (ID50=1.0 mg/kg), lipopolysaccharide-induced pyresis (ID50=0.24 mg/kg), and adjuvant-induced arthritis (ID50=0.74 mg/kg/day) in rodent models. Rofecoxib also protects adjuvant-induced destruction of cartilage and bone structures in rats. In a 51Cr excretion assay for detection of gastrointestinal integrity in either rats or squirrel monkeys, rofecoxib shows no effect at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day for 5 days. Rofecoxib (15 mg/kg, i.p.) reduces the blood vessels attached to the internal limiting membrane (ILM) in mice. COX-2 and VEGF protein expressions, COX-2 mRNA and VEGF mRNA are also significantly decreased by Rofecoxib in ROP mice.
-
SynonymsMK-0996 | MK-966
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetCOX
-
RecptorCOX-2
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
IndicationPain
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number162011-90-7
-
Formula Weight314.3557
-
Molecular FormulaC17H14O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
SMILESO=C1C(C2=CC=CC=C2)=C(C3=CC=C(S(=O)(C)=O)C=C3)CO1
-
Chemical Name2(5H)-Furanone, 4-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-3-phenyl-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Chan CC, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Aug;290(2):551-60.
2. Ehrich EW, et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Mar;65(3):336-47.
3. Prasit P, et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Jul 5;9(13):1773-8.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tolfenamic Acid
Tolfenamic acid (TA) is one of the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
-
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a phytoalexin produced naturally by several plants with anti-Y, anti-inflammatory, blood-sugar-lowering and other beneficial cardiovascular effects.
-
Deracoxib
A selective COX-2 inhibitor that is a non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


