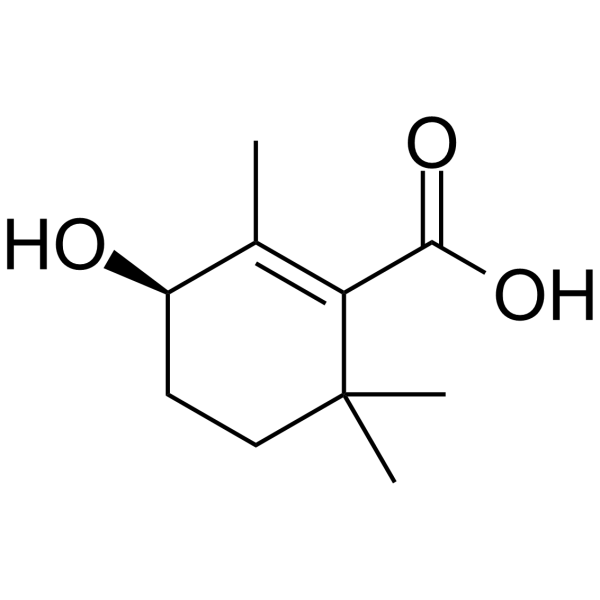
Rehmapicrogenin
CAS No. 135447-39-1
Rehmapicrogenin( —— )
Catalog No. M32309 CAS No. 135447-39-1
Rehmapicrogenin regulates the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway is the most important pathway of oxidative stress.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 1160 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRehmapicrogenin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRehmapicrogenin regulates the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway is the most important pathway of oxidative stress.
-
DescriptionRehmapicrogenin regulates the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway is the most important pathway of oxidative stress.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number135447-39-1
-
Formula Weight184.2
-
Molecular FormulaC10H16O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
IRONE
Irone is used as a fragrance ingredient.
-
Mezagitamab
Mezagitamab (TAK-079) is a fully humanized IgG1λ monoclonal antibody against CD38 with high affinity for CD38-expressing cells (including plasma mother cells, plasma cells, and natural killer cells).
-
CGS 20625
CGS 20625 is an orally active, specific, and potent partial agonist at the central benzodiazepine receptor with anxiolytic and anticonvulsant activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


