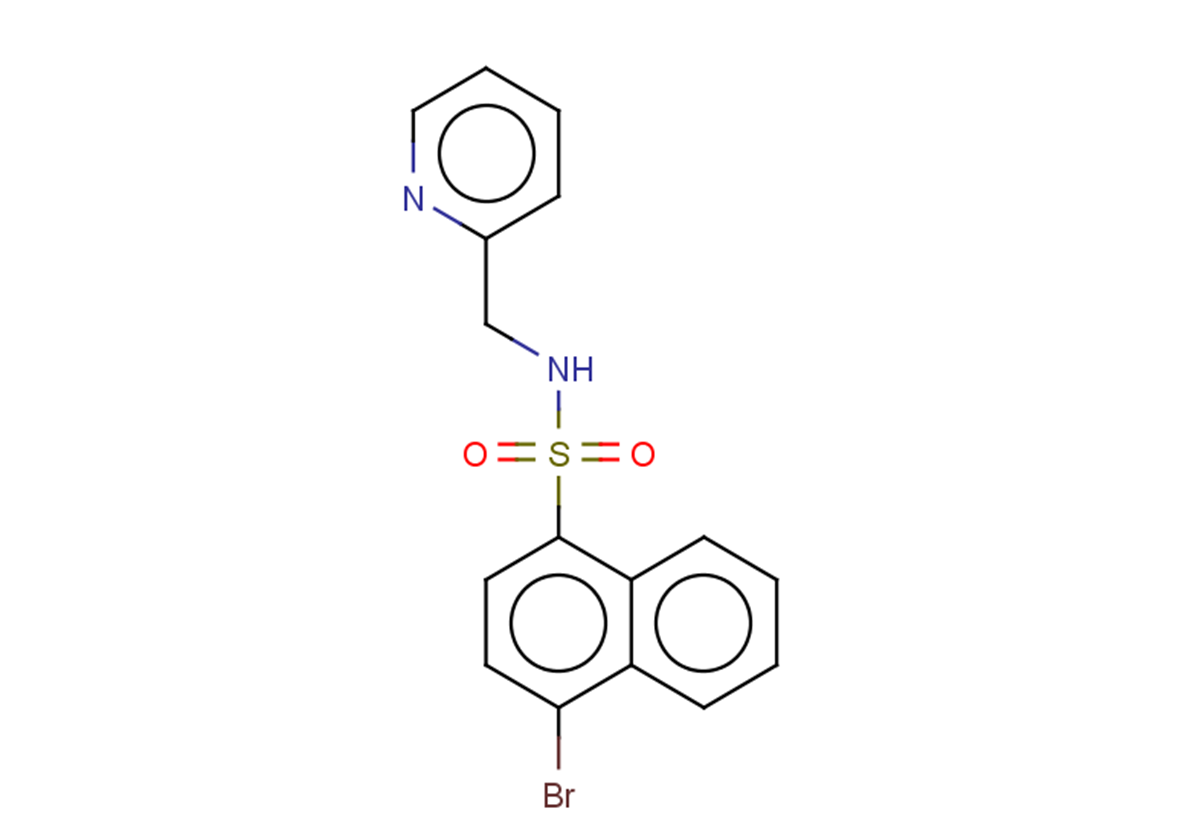
Pyrabactin
CAS No. 419538-69-5
Pyrabactin( —— )
Catalog No. M24382 CAS No. 419538-69-5
Pyrabactin is a seed-selective abscisic acid (ABA) agonist, Novel PYL agonist; acting as a plant growth inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 123 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 176 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 302 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePyrabactin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPyrabactin is a seed-selective abscisic acid (ABA) agonist, Novel PYL agonist; acting as a plant growth inhibitor.
-
DescriptionPyrabactin is a seed-selective abscisic acid (ABA) agonist, Novel PYL agonist; acting as a plant growth inhibitor.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorPYR/PYL/RCARs
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number419538-69-5
-
Formula Weight377.26
-
Molecular FormulaC16H13BrN2O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10mg/mL (26.50 mM)
-
SMILESO=S(c(c1ccccc11)ccc1Br)(NCc1ncccc1)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.González-Villagra J, et al. Evaluating the involvement and interaction of abscisic acid and miRNA156 in the induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in drought-stressed plants. Planta. 2017 May 22.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Kojibiose
Kojibiose is a disaccharide in honey. Kojibiose is a product of the caramelization of glucose.
-
GHRF, ovine
GHRF, ovine
-
Glycerol Tridecanoat...
Glycerol Tridecanoate is also known as triacylglycerols or triacylglycerides. The triglycerides are rebuilt in the blood from their fragments and become constituents of lipoproteins which deliver the fatty acids to and from fat cells among other functions. Various tissues can release free fatty acids and take them up as a source of energy.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


