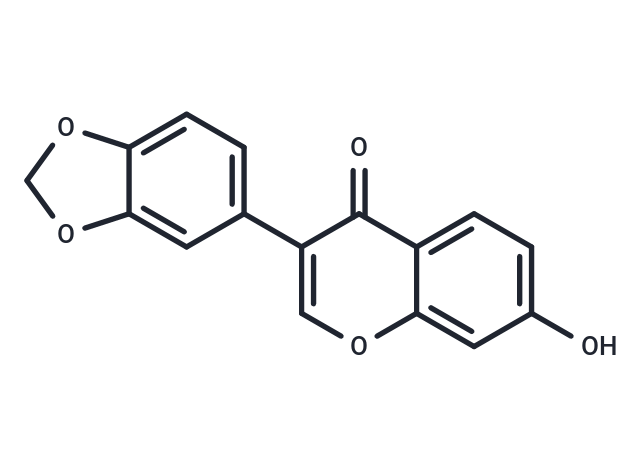
Pseudobaptigenin
CAS No. 90-29-9
Pseudobaptigenin( —— )
Catalog No. M37844 CAS No. 90-29-9
Pseudobaptigenin (Psi-baptigenin) is an isoflavone, a flavonoid lipid molecule that is a natural product found in Pterocarpus marsupium, Dalbergia spruceana.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 260 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 362 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 539 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 821 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePseudobaptigenin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPseudobaptigenin (Psi-baptigenin) is an isoflavone, a flavonoid lipid molecule that is a natural product found in Pterocarpus marsupium, Dalbergia spruceana.
-
DescriptionPseudobaptigenin is a flavonoid. Pseudobaptigenin shows very good anticataract activity. Pseudobaptigenin has good binding affinity for the inhibition of glycation against γ-crystallin protein. Pseudobaptigenin also has good ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Toxicity) property.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number90-29-9
-
Formula Weight282.25
-
Molecular FormulaC16H10O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C1C(C=2C=C3C(=CC2)OCO3)=COC=4C1=CC=C(O)C4
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Jeevanandam J, et al. Identification of potential phytochemical lead against diabetic cataract: An insilico approach. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2020, 1226.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pannexin - 1 Fragmen...
Pannexin - 1 Fragment (4515)
-
Chlorogenin
Chlorogenin is a natural steroid derived from the herbs of Agave americana.
-
2-Hydroxydaidzein
2'-Hydroxydaidzein is an isoflavonoid phytonutrient found in plant species, when a natural compound. 2'-Hydroxydaidzein has antioxidant activity, driven mainly by o-hydrogen bond dissociation enthalpy (BDE) and hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) mechanisms.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


