Prexasertib
CAS No. 1234015-52-1
Prexasertib( LY-2606368 | LY 2606368 | LY2606368 )
Catalog No. M10928 CAS No. 1234015-52-1
A potent, selective, ATP-competitive inhibitor of CHK1 with Ki of 0.9 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 111 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 173 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 339 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 497 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 708 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1431 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePrexasertib
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA potent, selective, ATP-competitive inhibitor of CHK1 with Ki of 0.9 nM.
-
DescriptionA potent, selective, ATP-competitive inhibitor of CHK1 with Ki of 0.9 nM; potently abrogates the G2-M checkpoint activated by doxorubicin in p53-deficient HeLa cells with EC50 of 9 nM; causes replication catastrophe in vitro and in vivo; shows significant tumor growth inhibition in xenograft tumor models.Lung Cancer Phase 2 Clinical(In Vitro):Prexasertib (LY2606368) inhibits MELK (IC50=38 nM), SIK (IC50=42 nM), BRSK2 (IC50=48 nM), ARK5 (IC50=64 nM). LY2606368 requires CDC25A and CDK2 to cause DNA damage.Prexasertib (33, 100 nM; for 7 hours) results in DNA damage during S-phase in HeLa cells.Prexasertib (8-250 nM; pre-treated for 15 minutes) inhibits CHK1 autophosphorylation (S296) and CHK2 autophosphorylation (S516) in HT-29 cells.Prexasertib (4 nM; 24 hours) results in a large shift in cell-cycle populations from G1 and G2-M to S-phase with an accompanied induction of H2AX phosphorylation in U-2 OS cells.Prexasertib (33 nM; for 12 hours) causes chromosomal fragmentation in HeLa cells. Prexasertib (100 nM; 0.5 to 9 hours) induces replication stress and depletes the pool of available RPA2 for binding to DNA.(In Vivo):Prexasertib (LY2606368; 1-10 mg/kg; SC; twice daily for 3 days, rest 4 days; for three cycles) causes growth inhibition in tumor xenografts.Prexasertib (15 mg/kg; SC) causes CHK1 inhibition in the blood and the phosphorylation of both H2AX (S139) and RPA2 (S4/S8).
-
In VitroPrexasertib (LY2606368) inhibits MELK (IC50=38 nM), SIK (IC50=42 nM), BRSK2 (IC50=48 nM), ARK5 (IC50=64 nM). LY2606368 requires CDC25A and CDK2 to cause DNA damage. Prexasertib (33, 100 nM; for 7 hours) results in DNA damage during S-phase in HeLa cells. Prexasertib (8-250 nM; pre-treated for 15 minutes) inhibits CHK1 autophosphorylation (S296) and CHK2 autophosphorylation (S516) in HT-29 cells. Prexasertib (4 nM; 24 hours) results in a large shift in cell-cycle populations from G1 and G2-M to S-phase with an accompanied induction of H2AX phosphorylation in U-2 OS cells. Prexasertib (33 nM; for 12 hours) causes chromosomal fragmentation in HeLa cells. Prexasertib (100 nM; 0.5 to 9 hours) induces replication stress and depletes the pool of available RPA2 for binding to DNA. Cell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:HeLa cells Concentration:33, 100 nM Incubation Time:For 7 hours Result:Had an IC50 of 37 nM and resulted in the G2-M population received DNA damage during S-phase but continued to progress through the cell cycle into an early mitosis.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:HT-29 cells Concentration:8, 16, 31, 63, 125, 250 nM.Incubation Time:Pre-treated for 15 minutes Result:Inhibited CHK1 autophosphorylation (S296) and CHK2 autophosphorylation (S516) (IC50 of less than 31 nM) in HT-29 cells.
-
In VivoPrexasertib (LY2606368; 1-10 mg/kg; SC; twice daily for 3 days, rest 4 days; for three cycles) causes growth inhibition in tumor xenografts. Prexasertib (15 mg/kg; SC) causes CHK1 inhibition in the blood and the phosphorylation of both H2AX (S139) and RPA2 (S4/S8). Animal Model:Female CD-1 nu-/nu- mice (26-28 g) with Calu-6 cells Dosage:1, 3.3, or 10 mg/kg Administration:SC; twice daily for 3 days, rest 4 days; for three cycles Result:Caused statistically significant tumor growth inhibition (up to 72.3%).Animal Model:Female CD-1 nu-/nu- mice (26-28 g) with Calu-6 cells Dosage:15 mg/kg (Pharmacokinetic Analysis)Administration:SC (200 μL) Result:CHK1 was 7 ng/mL at 12 hours and 3 ng/mL by 24 hours in plasma exposures.Phosphorylation of both H2AX (S139) and RPA2 (S4/S8) was detectable at 4 hours, showing the rapid occurrence of DNA damage.
-
SynonymsLY-2606368 | LY 2606368 | LY2606368
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetChk
-
RecptorChk1,Chk2
-
Research AreaCancer
-
IndicationLung Cancer
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1234015-52-1
-
Formula Weight365.3892
-
Molecular FormulaC18H19N7O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 60 mg/mL
-
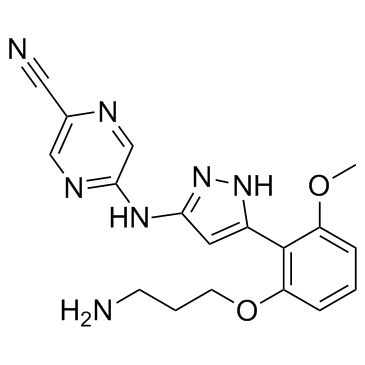
SMILESCOC1=C(C(=CC=C1)OCCCN)C2=CC(=NN2)NC3=NC=C(N=C3)C#N
-
Chemical Name2-Pyrazinecarbonitrile, 5-[[5-[2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]amino]-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. King C, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Sep;14(9):2004-13.
2. Lowery CD, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 1;23(15):4354-4363.
3. Sen T, et al. Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 15;77(14):3870-3884.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Baricitinib
Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050) is a selective JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor with IC50 of 5.9 nM and 5.7 nM in cell-free assays.
-
SB-218078
A potent inhibitor of Chk1 that blocks phosphorylation of cdc25 with IC50 of 15 nM.
-
GDC0575 monohydrochl...
GDC-0575 is a potent and selective inhibitor of cell cycle checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) with an IC50 of 1.2?nM. GDC-0575 specifically binds to and inhibits Chk1; this may result in tumor cells bypassing Chk1-dependent cell cycle arrest in the S and G2/M phases, which permits the cells to undergo DNA repair prior to entry into mitosis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


