Piprozolin
CAS No. 17243-64-0
Piprozolin( —— )
Catalog No. M34681 CAS No. 17243-64-0
Piprozolin (W 3699) is a new type of choleretic acid that shows slight analgesic properties at high doses during chronic experiments.Piprozolin has a slight induction of certain enzymes of the oxidative system.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 217 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 342 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 504 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 790 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1086 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1431 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 2871 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePiprozolin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPiprozolin (W 3699) is a new type of choleretic acid that shows slight analgesic properties at high doses during chronic experiments.Piprozolin has a slight induction of certain enzymes of the oxidative system.
-
DescriptionPiprozolin (W 3699) is a new type of choleretic acid that shows slight analgesic properties at high doses during chronic experiments.Piprozolin has a slight induction of certain enzymes of the oxidative system.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number17243-64-0
-
Formula Weight298.4
-
Molecular FormulaC14H22N2O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
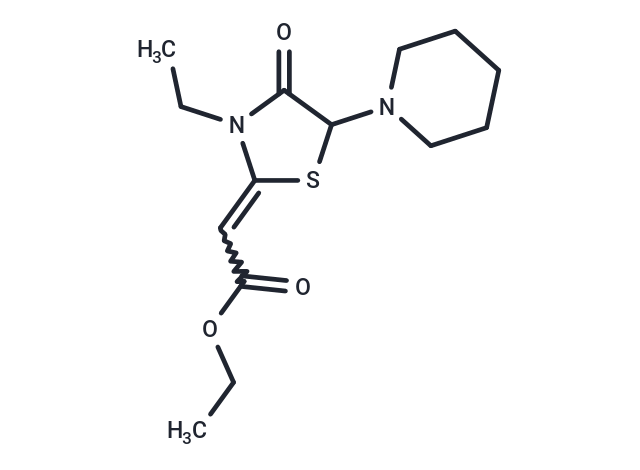
SMILESO=C1C(SC(=CC(OCC)=O)N1CC)N2CCCCC2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
(S,R,S)-AHPC-PEG2-NH...
(S,R,S)-AHPC-PEG2-NH2 hydrochloride (VH032-PEG2-NH2 hydrochloride) is a synthesized E3 ligase ligand-linker conjugate that incorporates the (S,R,S)-AHPC based VHL ligand and 2-unit PEG linker used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
Cornoside
Cornoside and Iridoids are chemosystematic markers.
-
LAH4
The a-helix of the amphipathic peptide antibiotic LAH4 (KKALLALALHHLAHLALHLALALKKA-NH2) strongly interacts with phospholipid membranes, demonstrating in vitro transfection efficiencies comparable to those of commercially available reagents.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


