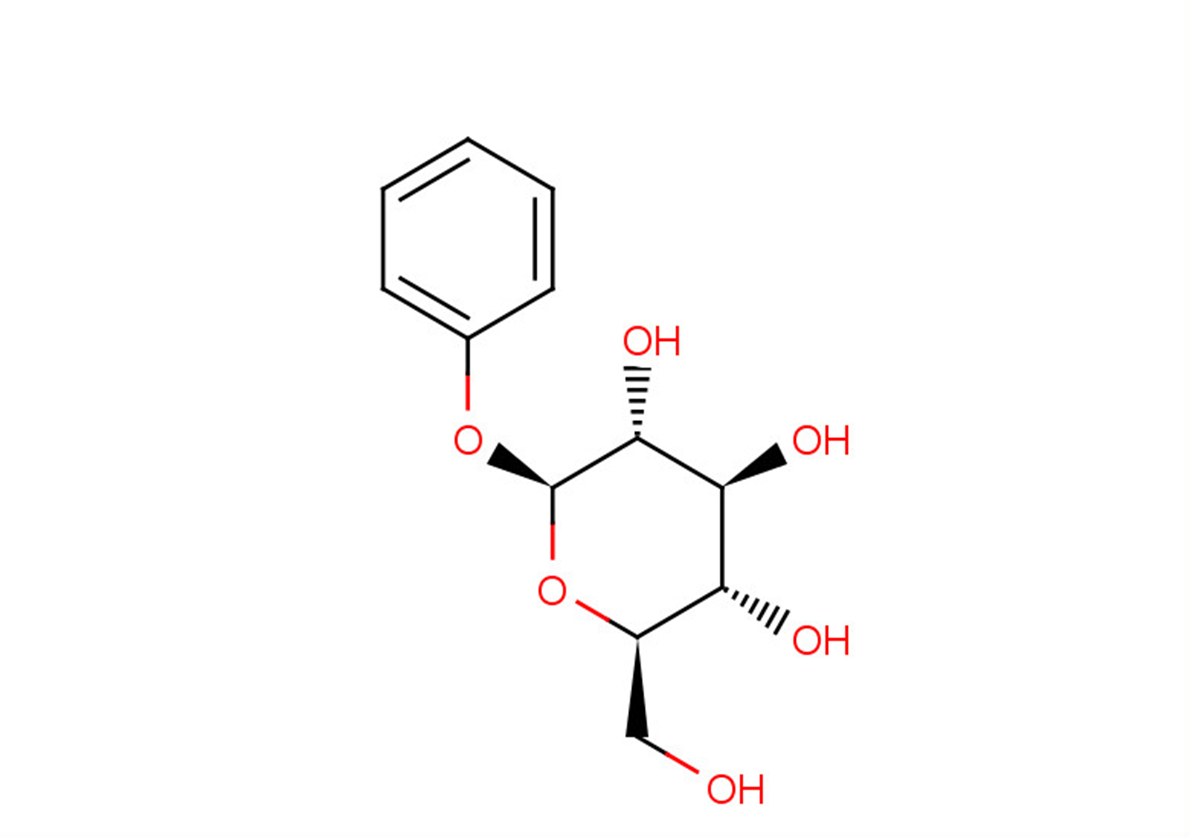
Phenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
CAS No. 1464-44-4
Phenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside( —— )
Catalog No. M23626 CAS No. 1464-44-4
Phenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside is a component of Phellodendron amurense with anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 200MG | 26 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePhenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPhenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside is a component of Phellodendron amurense with anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities.
-
DescriptionPhenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside is a component of Phellodendron amurense with anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1464-44-4
-
Formula Weight256.25
-
Molecular FormulaC12H16O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater:soluble
-
SMILESO[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O1)O)O)[C@@H]1OC2=CC=CC=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hwang SJ, Lee HJ. Phenyl-β-D-Glucopyranoside Exhibits Anti-inflammatory Activity in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated RAW 264.7 Cells. Inflammation. 2015;38(3):1071-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
[Tyr12]-Somatostatin...
[Tyr12]-Somatostatin-28 (1-14)
-
Cyperotundone
Cyperotundone is a natural product from Cyperus rotundus.
-
N-Methyltaurine
N-Methyltaurine is a useful organic compound for research related to life sciences.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


