Pepstatin
CAS No. 26305-03-3
Pepstatin( NSC 272671 | Pepsin Inhibitor S 735A )
Catalog No. M13803 CAS No. 26305-03-3
Pepstatin is a potent inhibitor of aspartyl proteases; inhibits the aspartic proteases cathepsin D, pepsin, and renin.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 149 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 246 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 357 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePepstatin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPepstatin is a potent inhibitor of aspartyl proteases; inhibits the aspartic proteases cathepsin D, pepsin, and renin.
-
DescriptionPepstatin is a potent inhibitor of aspartyl proteases; inhibits the aspartic proteases cathepsin D, pepsin, and renin.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoAnimal Model:Pylorus ligated male Wistar rats Dosage:0.5, 1, 10 and 50 mg/kg Administration:Oral administration, 15 minutes after pyloric ligation Result:Effectively prevented stomach ulceration.
-
SynonymsNSC 272671 | Pepsin Inhibitor S 735A
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetAmino Acids and Derivatives
-
Recptoraspartic protease
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number26305-03-3
-
Formula Weight685.89
-
Molecular FormulaC34H63N5O9
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 100 mg/mL (145.79 mM)
-
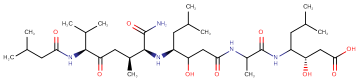
SMILESC[C@@H](CC([C@H](C(C)C)NC(CC(C)C)=O)=O)[C@@H](C(N)=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(O)CC(NC(C)C(NC([C@@H](O)CC(O)=O)CC(C)C)=O)=O
-
Chemical Name(3S,12S,14S,15S,18S)-14-carbamoyl-3,11-dihydroxy-4,12-diisobutyl-18-isopropyl-7,15,22-trimethyl-6,9,17,20-tetraoxo-5,8,13,19-tetraazatricosanoic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Seelmeier S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988, 85(18), 6612-6616.
molnova catalog



related products
-
L-Ornithine
L-ornithine has an antifatigue effect in increasing the efficiency of energy consumption and promoting the excretion of ammonia.
-
4-Aminohippuric Acid
4-Aminohippuric acid is a typical substrate of organic anion transport systems.
-
Fmoc-L-aspartic acid
Fmoc-L-aspartic acid (Fmoc-Asp-OH) is an aspartic acid derivative.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


