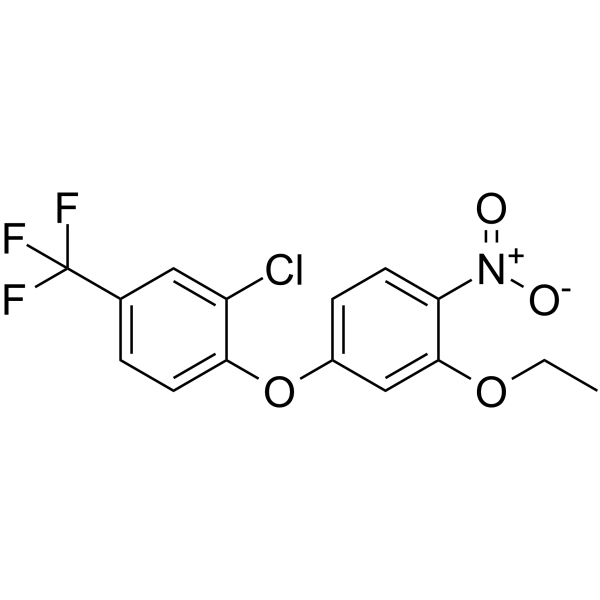
Oxyfluorfen
CAS No. 42874-03-3
Oxyfluorfen( Boxer | Galigan | Goldate | Koltar | RH-2915 | RH 2915 )
Catalog No. M27307 CAS No. 42874-03-3
Oxyfluorfen, a herbicide of the nitrodiphenyl ether class, is used to control annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and sedges in a variety of field crops.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 51 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 86 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 157 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameOxyfluorfen
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionOxyfluorfen, a herbicide of the nitrodiphenyl ether class, is used to control annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and sedges in a variety of field crops.
-
DescriptionOxyfluorfen, a herbicide of the nitrodiphenyl ether class, is used to control annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and sedges in a variety of field crops.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBoxer | Galigan | Goldate | Koltar | RH-2915 | RH 2915
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorALK5
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number42874-03-3
-
Formula Weight361.7
-
Molecular FormulaC15H11ClF3NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCCOc1cc(Oc2ccc(cc2Cl)C(F)(F)F)ccc1[N+]([O-])=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Scutebarbatine A
Scutebarbatine A shows significant antitumor effects on A549 cells in vivo and in vitro via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by up-regulating expressions of caspase-3 and 9, and down-regulating Bcl-2.
-
Benzocaine hydrochlo...
Benzocaine hydrochloride is a surface anesthetic that acts by preventing transmission of impulses along nerve fibers and at nerve endings.
-
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidines are heterocyclic six-membered nitrogen-containing carbon ring structures with uracil cytosine and thymine being the basal structures of ribose-containing nucleosides (uridine cytidine and thymidine respectively) or deoxyribose-containing deoxynucleosides and their corresponding ribonucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


