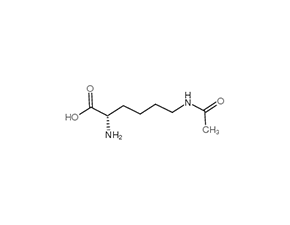
Nepsilon-Acetyl-L-lysine
CAS No. 692-04-6
Nepsilon-Acetyl-L-lysine( —— )
Catalog No. M21405 CAS No. 692-04-6
Nepsilon-Acetyl-L-lysine is a derivative of the amino acid lysine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 38 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNepsilon-Acetyl-L-lysine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNepsilon-Acetyl-L-lysine is a derivative of the amino acid lysine.
-
DescriptionNepsilon-Acetyl-L-lysine is a derivative of the amino acid lysine.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number692-04-6
-
Formula Weight188.22
-
Molecular FormulaC8H16N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O:37 mg/mL (196.57 mM)
-
SMILESCC(NCCCC[C@@H](C(O)=O)N)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Schmidt H et al. Characterization of a novel enzyme N6-acetyl-L-lysine: 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase which catalyses the second step of lysine catabolism in Candida maltosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1992 Nov;62(4):285-90.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nonan-5-ol
Nonan-5-ol (5-nonanol) can be used to synthesize molecular imprinting pseudo-template polymers.
-
Glaucoside A
Glaucoside A is a natural product for research related to life sciences.
-
Lariciresinol 4-O-gl...
The roots of Stellera chamaejasme L.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


