NSI-189
CAS No. 1270138-40-3
NSI-189( NSI-189 | NSI 189 | NSI189 )
Catalog No. M11133 CAS No. 1270138-40-3
NSI-189 is a nootropic and neurogenic research chemical derived from nicotinamide and pyrazine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 58 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 102 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 178 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 312 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 537 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNSI-189
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNSI-189 is a nootropic and neurogenic research chemical derived from nicotinamide and pyrazine.
-
DescriptionNSI-189 is a nootropic and neurogenic research chemical derived from nicotinamide and pyrazine.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsNSI-189 | NSI 189 | NSI189
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1270138-40-3
-
Formula Weight366.5
-
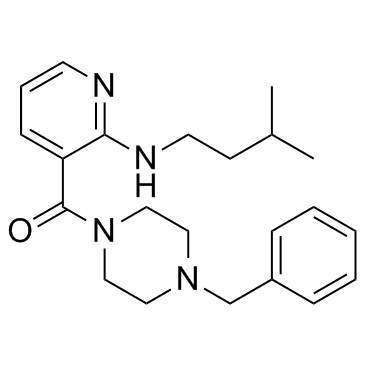
Molecular FormulaC22H30N4O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
SMILESO=C(N1CCN(CC2=CC=CC=C2)CC1)C3=CC=CN=C3NCCC(C)C
-
Chemical Name(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)(2-(isopentylamino)pyridin-3-yl)methanone
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Compositions to effect neuronal growth US 8030492 B2
molnova catalog



related products
-
L-Alaninol
L-Alaninol (2-Aminopropanol) is a pharmaceutical intermediate used in the manufacture of Ofloxacin.
-
Methyl (E)-oct-2-eno...
Methyl (E)-oct-2-enoate (Methyl trans-2-octenoate) is a volatile substance found in melons and fruits and is a flavor.
-
Kaempferol 3-O-beta-...
Kaempferol 3-O-beta-(6''-p-coumaroyl)glucopyranosyl(1->2)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside is a natural product.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


