NIC3
CAS No. 494830-67-0
NIC3( —— )
Catalog No. M26332 CAS No. 494830-67-0
NIC3 is a selective nucleus accumbens-associated protein-1 (NAC1) inhibitor, with anti-cancer activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 58 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 177 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 282 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 484 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 677 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1035 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNIC3
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNIC3 is a selective nucleus accumbens-associated protein-1 (NAC1) inhibitor, with anti-cancer activity.
-
DescriptionNIC3 is a selective nucleus accumbens-associated protein-1 (NAC1) inhibitor, with anti-cancer activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorPEGs
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number494830-67-0
-
Formula Weight440.58
-
Molecular FormulaC26H36N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (113.49 mM)
-
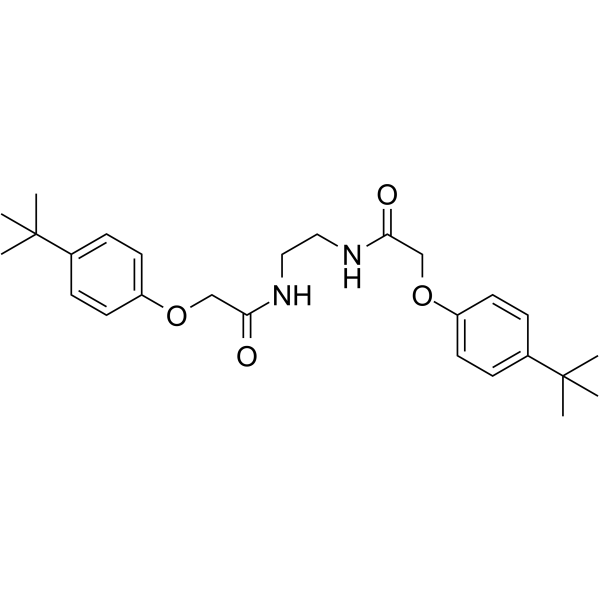
SMILESCC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(OCC(NCCNC(COC2=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C2)=O)=O)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.An S, et al. Small-molecule PROTACs: An emerging and promising approach for the development of targeted therapy drugs. EBioMedicine. 2018 Oct;36:553-562
molnova catalog



related products
-
Licoricesaponin G2
Licoricesaponin G2 is a pentacyclic triterpenoid derived from Glycyrrhiza aspera, which can be used to differentiate crude liquorice from honey-processed liquorice.
-
2-Methylbenzhydrol
Used as pharmaceutical intermediates.
-
Bletilloside A
Bletilloside A is a natural product for research related to life sciences.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


