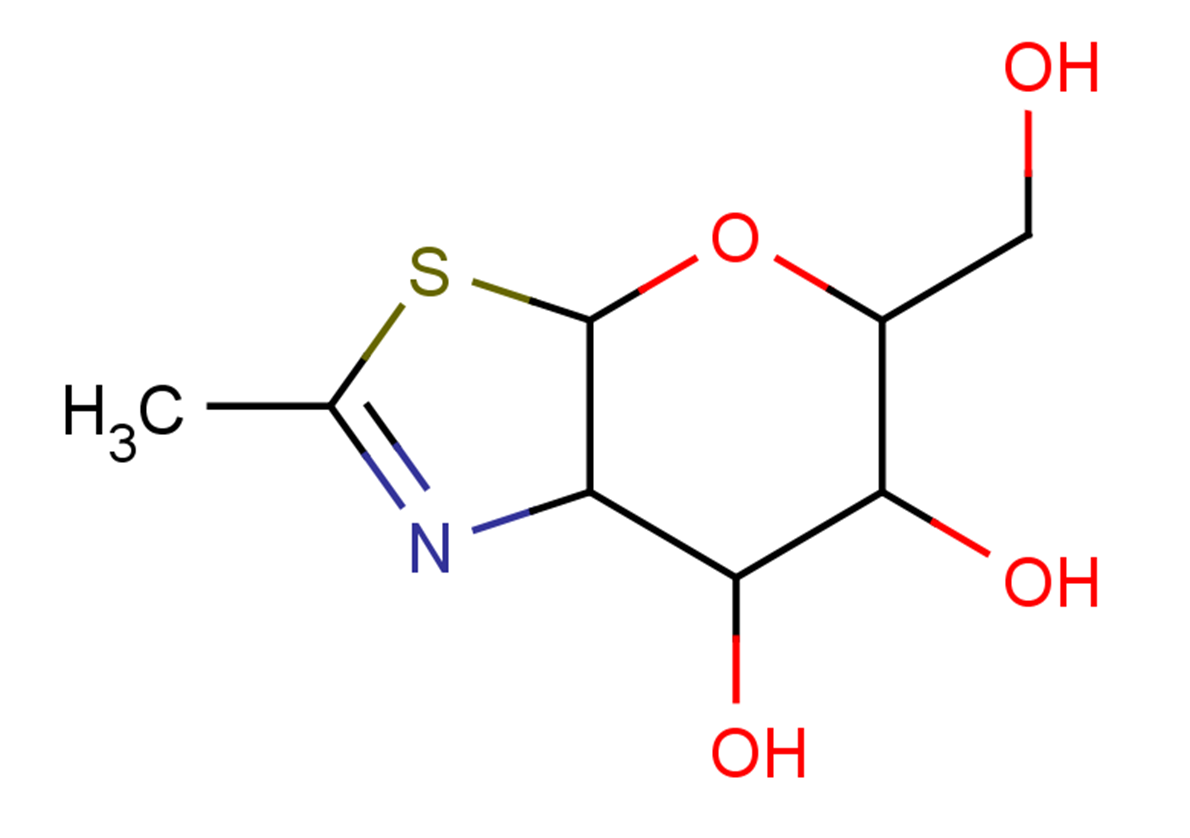
NAG-thiazoline
CAS No. 179030-22-9
NAG-thiazoline( GlcNAc-thiazoline )
Catalog No. M23803 CAS No. 179030-22-9
NAG-thiazoline is an O-GlcNAcase inhibitor with Ki value of 180 nM. It is active against V. campbellii with MIC value of 0.5 μM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 80 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 170 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 250 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 407 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNAG-thiazoline
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNAG-thiazoline is an O-GlcNAcase inhibitor with Ki value of 180 nM. It is active against V. campbellii with MIC value of 0.5 μM.
-
DescriptionNAG-thiazoline is an O-GlcNAcase inhibitor with Ki value of 180 nM. It is active against V. campbellii with MIC value of 0.5 μM.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsGlcNAc-thiazoline
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorO-GlcNAcase|VhGlcNAcase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number179030-22-9
-
Formula Weight219.26
-
Molecular FormulaC8H13NO4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (456.08 mM)
-
SMILESCC(SC1OC(CO)C2O)=NC1C2O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.NAG‐thiazoline is a potent inhibitor of the Vibriocampbellii GH20 β‐N‐Acetylglucosaminidase[J]. FEBS Journal, 2020.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Hexadecyl propionate
Hexadecyl propionate is often used as a solvent or stabilizer component in spices and flavors.
-
Eptifibatide acetate
Eptifibatide an antiplatelet drug of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor class is a cyclic heptapeptide constructed from 6 amino acids and a mercaptopropionyl residue.
-
Murrayanine
Murrayanine is a natural product isolated from leaves and stems of Murraya kwangsiensis (C.C. Huang) C.C. Huang (Rutaceae).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


