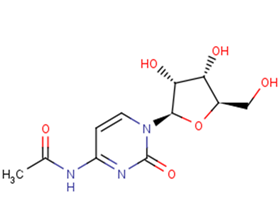
N4-Acetylcytidine
CAS No. 3768-18-1
N4-Acetylcytidine( —— )
Catalog No. M19336 CAS No. 3768-18-1
N4-Acetylcytidine is a modified nucleoside. N4-acetylcytidine is an endogenous urinary nucleoside product of the degradation of transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameN4-Acetylcytidine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionN4-Acetylcytidine is a modified nucleoside. N4-acetylcytidine is an endogenous urinary nucleoside product of the degradation of transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA).
-
DescriptionN4-Acetylcytidine is a modified nucleoside. N4-acetylcytidine is an endogenous urinary nucleoside product of the degradation of transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA); urinary nucleosides are biological markers for patients with colorectal cancer.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3768-18-1
-
Formula Weight285.25
-
Molecular FormulaC11H15N3O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (87.64 mM)
-
SMILESCC(=O)NC1=NC(=O)N(C=C1)[C@@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zheng YF,etal.Urinary nucleosides as biological markers for patients with colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jul 7;11(25):3871-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nodakenetin
Nodakenetin has clinical efficacy.
-
Biotin-Phosphorylate...
Biotin-Phosphorylated MBP (94 - 102)
-
Phthalic Acid Monobe...
Used as organic synthesis and medicine intermediate.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


