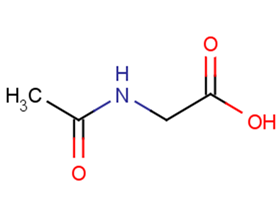
N-Acetylglycine
CAS No. 543-24-8
N-Acetylglycine( Aceturic acid | Acetamidoacetic acid )
Catalog No. M19625 CAS No. 543-24-8
N-Acetylglycine is a minor constituent of numerous foods with no genotoxicity or acute toxicity. N-acetylglycine is used in biological research of peptidomimetics.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameN-Acetylglycine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionN-Acetylglycine is a minor constituent of numerous foods with no genotoxicity or acute toxicity. N-acetylglycine is used in biological research of peptidomimetics.
-
DescriptionN-Acetylglycine is a minor constituent of numerous foods with no genotoxicity or acute toxicity. N-acetylglycine is used in biological research of peptidomimetics.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAceturic acid | Acetamidoacetic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number543-24-8
-
Formula Weight117.1
-
Molecular FormulaC4H7NO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM;Water: 27 mg/mL
-
SMILESCC(=O)NCC(O)=O
-
Chemical NameGlycine N-acetyl-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Harper MS et al. Toxicology studies with N-acetylglycine. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 May;48(5):1321-7.
molnova catalog



related products
-
7-O-Acetylintermedin...
7-O-Acetylintermedine-N-oxide is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid isolated from Symphytum officinale.
-
Tanshinone IIA-sulfo...
Extracted from Savia miltiorrhiza.
-
beta-estradiol 17-ac...
beta-estradiol 17-acetate is a metabolite of estradiol.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


