Menbutone
CAS No. 3562-99-0
Menbutone( Menbutone | Epanaftol | Fel-Bis | Genabil | Genabilin | Membutona | Menbutonum | Naftobil | SC 1749 )
Catalog No. M14222 CAS No. 3562-99-0
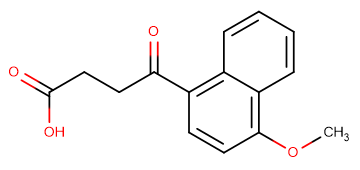
Menbutone is an organic compound with fomula C15H14O4.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMenbutone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMenbutone is an organic compound with fomula C15H14O4.
-
DescriptionMenbutone is an organic compound with fomula C15H14O4.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsMenbutone | Epanaftol | Fel-Bis | Genabil | Genabilin | Membutona | Menbutonum | Naftobil | SC 1749
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3562-99-0
-
Formula Weight258.27
-
Molecular FormulaC15H1404
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
SMILESO=C(O)CCC(C1=C2C=CC=CC2=C(OC)C=C1)=O
-
Chemical Name4-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-4-oxobutanoic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Lund J, Lassen JB. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1969; 27(6):429-38.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Biotin-Obestatin (hu...
Biotin-Obestatin (human)
-
Competence-Stimulati...
Competence-Stimulating Peptide-12261, a sixteen peptide, is a fragment of competence-stimulating peptide.
-
Mannose
D-Mannose is a hexose or fermentable monosaccharide and isomer of glucose from manna, the ash Fraxinus ornus and related plants.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


