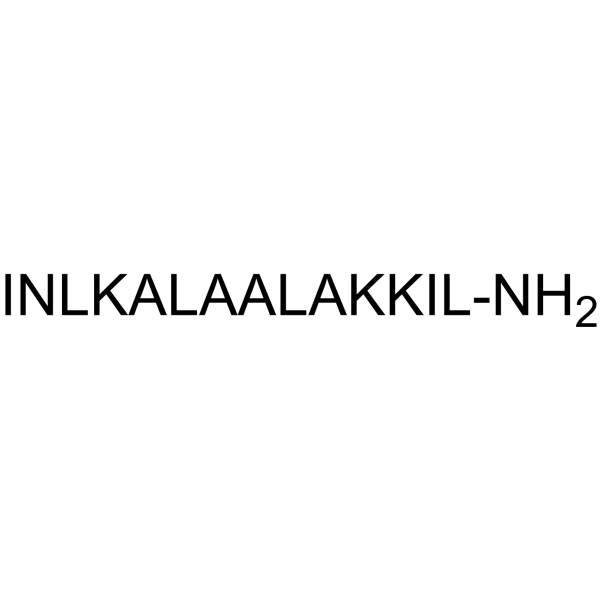
Mastoparan
CAS No. 72093-21-1
Mastoparan( —— )
Catalog No. M30085 CAS No. 72093-21-1
Mastoparan is a peptide toxin from wasp venom. It has the chemical structure Ile-Asn-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Ala-Ala-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Ile-Leu-NH2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 320 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 498 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 842 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMastoparan
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMastoparan is a peptide toxin from wasp venom. It has the chemical structure Ile-Asn-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Ala-Ala-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Ile-Leu-NH2.
-
DescriptionMastoparan is a peptide toxin from wasp venom. It has the chemical structure Ile-Asn-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Ala-Ala-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Ile-Leu-NH2. (In Vitro):Mastoparan has an amphiphilic nature and is reported to exert a variety of pharmacological and biochemical effects. Mastoparan induces exocytosis of hormones from anterior pituitary cells. Mastoparan stimulation of prolactin secretion is dose-dependent, time-dependent, reversible and required the presence of calcium. Mastoparan causes translocation of protein kinase C activity from a soluble to a membrane-attached form. Mastoparan is able to increase the intracellular Ca2+ concentration in Fura-2-loaded individual lactotrophs. Mastoparan is also able to interact with GTP-bindmg proteins. Thus, Mastoparan has been shown to facilitate exchange of nucleotides and to stimulate GTPase activity on G-proteins. It has therefore been proposed that the cellular effects of Mastoparan are due to an ability to mimic G-protein-linked agonist-liganded receptors.
-
In VitroMastoparan has an amphiphilic nature and is reported to exert a variety of pharmacological and biochemical effects. Mastoparan induces exocytosis of hormones from anterior pituitary cells. Mastoparan stimulation of prolactin secretion is dose-dependent, time-dependent, reversible and required the presence of calcium. Mastoparan causes translocation of protein kinase C activity from a soluble to a membrane-attached form. Mastoparan is able to increase the intracellular Ca2+ concentration in Fura-2-loaded individual lactotrophs.Mastoparan is also able to interact with GTP-bindmg proteins. Thus, Mastoparan has been shown to facilitate exchange of nucleotides and to stimulate GTPase activity on G-proteins. It has therefore been proposed that the cellular effects of Mastoparan are due to an ability to mimic G-protein-linked agonist-liganded receptors.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number72093-21-1
-
Formula Weight1478.91
-
Molecular FormulaC70H131N19O15
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O : 33.33 mg/mL (22.54 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical NameSequence:Ile-Asn-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Ala-Ala-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Ile-Leu-NH2
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
Mau SE, et al. Mastoparan, a wasp venom peptide, stimulates release of prolactin from cultured rat anterior pituitary cells. J Endocrinol. 1994 Jul;142(1):9-18.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Trimethylvinylammoni...
Reference standards.
-
Brassinolide
Brassinolide is a plant hormone. The first isolated brassinosteroid, it was discovered when it was shown that pollen from rapeseed (Brassica napus) could promote stem elongation and cell division.
-
AST 7062601
AST 7062601 is a potent Ucp1 inducer that promotes endogenous Ucp1 expression in primary mouse brown adipocytes.AST 7062601 may be useful in the study of obesity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


