MAC168425
CAS No. 2138-33-2
MAC168425( MAC 168425 )
Catalog No. M13407 CAS No. 2138-33-2
MAC168425 is a novel antibacterial inhibitor that interferes with glycine metabolism in E coli.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMAC168425
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMAC168425 is a novel antibacterial inhibitor that interferes with glycine metabolism in E coli.
-
DescriptionMAC168425 is a novel antibacterial inhibitor that interferes with glycine metabolism in E coli.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsMAC 168425
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorAntibacterial
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2138-33-2
-
Formula Weight207.273
-
Molecular FormulaC12H17NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
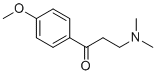
SMILESCN(C)CCC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC
-
Chemical Name3-(dimethylamino)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-1-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Zlitni S, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2013 Dec;9(12):796-804.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ethyl acetoacetate
Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate), an ester, is a bacterial biofilm inhibitor and an intermediate utilized in the synthesis of various compounds.
-
Meropenem trihydrate
Meropenem trihydrate with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity,is a carbapenem antibiotic.
-
PAβN dihydrochloride
PAβN dihydrochloride is an inhibitor of efflux pump. PAβN reduces the MICs in nine ciprofloxacin-resistant isolates, and in four of these, PAβN increases the susceptibility by twofold.?



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


