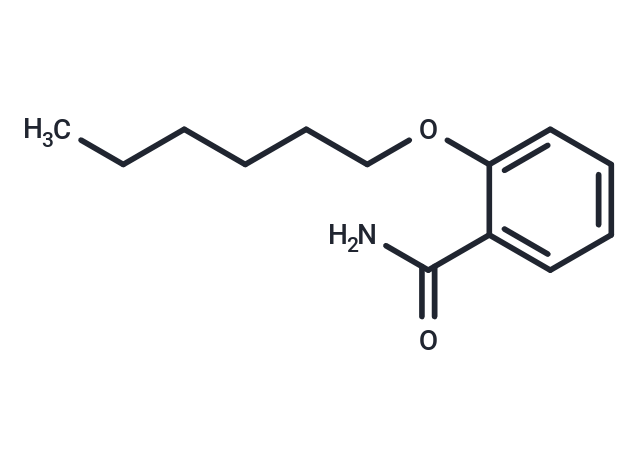
Exalamide
CAS No. 53370-90-4
Exalamide( —— )
Catalog No. M37949 CAS No. 53370-90-4
Exalamide (2-(Hexyloxy)benzamide) is an aromatic amide with antifungal activity used in the study of dermatophytes.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 142 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameExalamide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionExalamide (2-(Hexyloxy)benzamide) is an aromatic amide with antifungal activity used in the study of dermatophytes.
-
DescriptionExalamide (2-(Hexyloxy)benzamide), an arenecarboxamide, is a potent antifungal agent.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetAntifungal
-
RecptorAntifungal
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number53370-90-4
-
Formula Weight221.3
-
Molecular FormulaC13H19NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (451.88 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCCCCCCOc1ccccc1C(N)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. T Kusunoki, et al. Comparison of the in vitro antifungal activities of clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole and exalamide against clinical isolates of dermatophytes. J Dermatol. 1984 Jun;11(3):277-81.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tenacissoside H
Tenacissoside H has antitumor activity on esophageal cancer through arresting cell cycle and regulating PI3K/Akt-NF-κB transduction cascade.
-
MoTPS1-IN-1
MoTPS1-IN-1 is a potent MoTPS1 inhibitor with antifungal and potentially anti-inflammatory activity that acts through interaction with Glu396 and can be used to study ulcerative colitis.
-
4-Methylcinnamic aci...
4-Methylcinnamic acid, a Cinnamic acid analog, can be used as a intervention catalyst for overcoming antifungal tolerance. 4-Methylcinnamic acid can improve the potency of cell wall-disrupting agents.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


