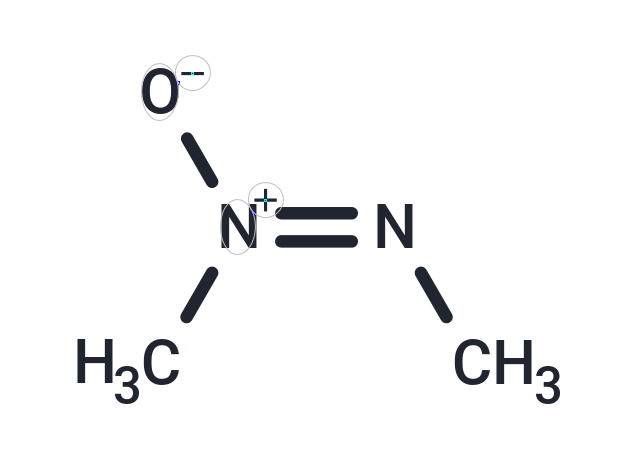
Azoxymethane
CAS No. 25843-45-2
Azoxymethane( —— )
Catalog No. M36563 CAS No. 25843-45-2
Azoxymethane (AOM) is a DNA damaging agent that induces cancer and can be used in mouse models of colorectal cancer.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 370 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 663 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAzoxymethane
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAzoxymethane (AOM) is a DNA damaging agent that induces cancer and can be used in mouse models of colorectal cancer.
-
DescriptionAzoxymethane is a colon carcinogen which leads to the formation of DNA adducts.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorDNA
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number25843-45-2
-
Formula Weight74.08
-
Molecular FormulaC2H6N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC\N=[N+](/C)[O-]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Megaraj V, et al. Role of hepatic and intestinal p450 enzymes in the metabolic activation of the colon carcinogen azoxymethane in mice. Chem Res Toxicol. 2014 Apr 21;27(4):656-62.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Datelliptium chlorid...
Datelliptium chloride hydrochloride is a DNA-intercalating agent derived from ellipticine. with anti-tumor activities.
-
Ddr1-In-1
DDR1-IN-1 is an effective and specific?DDR1?receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (IC50: 105 nM), about 3-fold selectivity over DDR2.
-
AS-136A
AS-136A is an orally active measles virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitor with antiviral activity that inhibits measles virus and blocks viral RNA synthesis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


