E-3620
CAS No. 151213-86-4
E-3620( —— )
Catalog No. M35619 CAS No. 151213-86-4
E-3620 is a novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist that inhibits cisplatin-induced vomiting in beagles. E-3620 can be used to study dyskinesia, gastrointestinal dyskinesia, psoriasis and psoriasis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 298 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameE-3620
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionE-3620 is a novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist that inhibits cisplatin-induced vomiting in beagles. E-3620 can be used to study dyskinesia, gastrointestinal dyskinesia, psoriasis and psoriasis.
-
DescriptionE-3620 is a potent 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. E-3620 can be used for the research of dyskinesi and gastrointestinal motility.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
Target5-HT Receptor
-
Recptor5-HT Receptor
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number151213-86-4
-
Formula Weight412.35
-
Molecular FormulaC20H27Cl2N3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (242.51 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
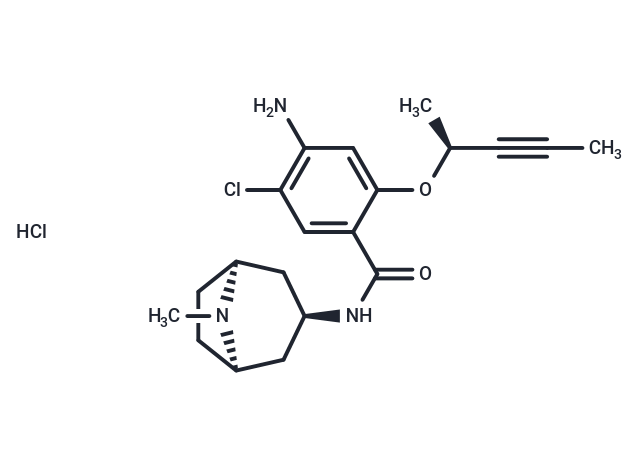
SMILESCl.CC#C[C@H](C)Oc1cc(N)c(Cl)cc1C(=O)N[C@@H]1C[C@@H]2CC[C@H](C1)N2C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. George Peter Arthur Rice. 5-ht3 receptor antagonists for dyskinesia. CA2231887A1.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ricasetron
Ricasetron (Brl 46470) is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist with pro-axonal lysis and antiemetic properties, and is used in the study of anxiety and anxiety disorders.
-
WAY-100635
A potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist; also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor.
-
Tabernanthalog
Tabernanthalog (TBG) is a 5-HT2A agonist. In rodents,Tabernanthalog has been found to promote structural neuroplasticity, reduce alcohol-seeking and heroin-seeking behavior, and produce antidepressant effects.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


