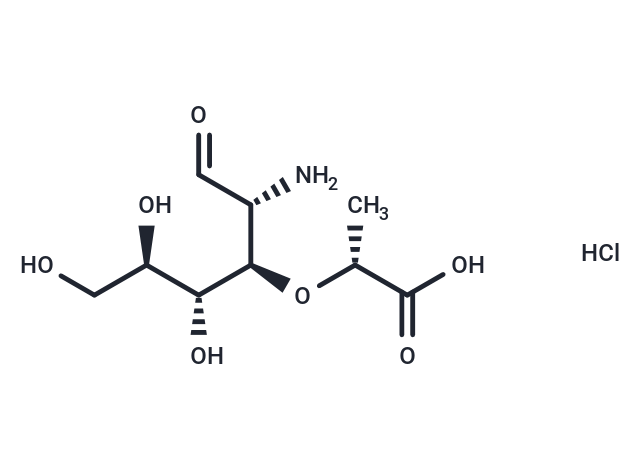
Muramic acid HCl
CAS No. 55226-93-2
Muramic acid HCl( —— )
Catalog No. M35015 CAS No. 55226-93-2
Muramic acid HCl is part of the peptidoglycan in the cell wall of many Gram-positive bacteria.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 459 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 657 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 1026 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMuramic acid HCl
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMuramic acid HCl is part of the peptidoglycan in the cell wall of many Gram-positive bacteria.
-
DescriptionMuramic acid HCl is part of the peptidoglycan in the cell wall of many Gram-positive bacteria.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number55226-93-2
-
Formula Weight287.7
-
Molecular FormulaC9H18ClNO7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)(O[C@@H](C(O)=O)C)[C@H](C=O)N.Cl
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
[pThr3]-CDK5 Substra...
[pThr3]-CDK5 Substrate TFA is an effective Phospho-Thr3CDK5 Substrate. [pThr3]-CDK5 Substrate is phosphorylated by CDK5 with a Km value of 6 μM.
-
Oxelumab
Oxelumab (R 4930) is a human monoclonal antibody targeting OX40L, and could be used to study asthma.
-
p-Phenylenediamine, ...
p-Phenylenediamine, N,N'-diphenyl- is a bioactive chemical. It has been used to prevent vitamin E deficiency in lambs.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


