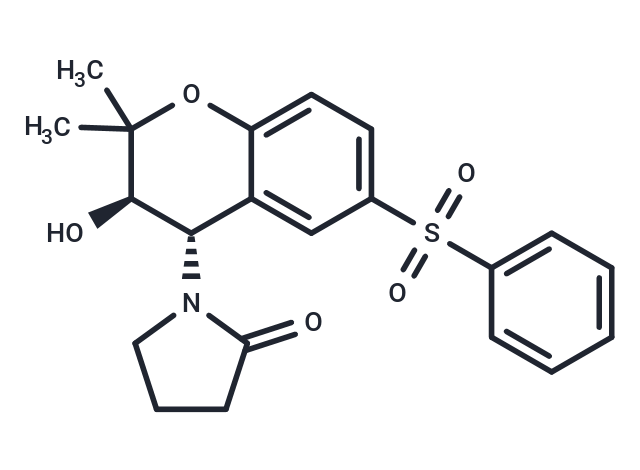
(Iso)-Rilmakalim
CAS No. 184653-89-2
(Iso)-Rilmakalim( —— )
Catalog No. M34130 CAS No. 184653-89-2
1-((3R,4S)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-6-(phenylsulfonyl)chroman-4-yl)pyrrolidin-2-one is an isomer of Rilmakalim, a potassium channel opener (PCO), which can activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the heart or other tissues
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 172 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 254 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 392 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 551 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name(Iso)-Rilmakalim
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1-((3R,4S)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-6-(phenylsulfonyl)chroman-4-yl)pyrrolidin-2-one is an isomer of Rilmakalim, a potassium channel opener (PCO), which can activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the heart or other tissues
-
Description1-((3R,4S)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-6-(phenylsulfonyl)chroman-4-yl)pyrrolidin-2-one is an isomer of Rilmakalim, a potassium channel opener (PCO), which can activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the heart or other tissues
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number184653-89-2
-
Formula Weight401.48
-
Molecular FormulaC21H23NO5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO[C@@H]1[C@H](C=2C(=CC=C(S(=O)(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3)C2)OC1(C)C)N4C(=O)CCC4
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Methylmalonic acid
Methylmalonate (MMA) is a dicarboxylic acid that can be derived from methylmalonyl-coenzyme A. It is an indicator of Vitamin B-12 deficiency in cancer.
-
(S)-(+)-2-Octanol
(S)-(+)-2-Octanol is the S-enantiomer of octan-2-ol. Octan-2-ol is involved in the production of nanomaterials and liquid crystal materials.
-
Pelargonidin3-O-[6-O...
Pelargonidin3-O-[6-O-(E)-P-coumarin-2-O-β-D-glucoside}-β-D-glucoside]-5-O-(6-O-malonyl)-β-D-glucoside



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


