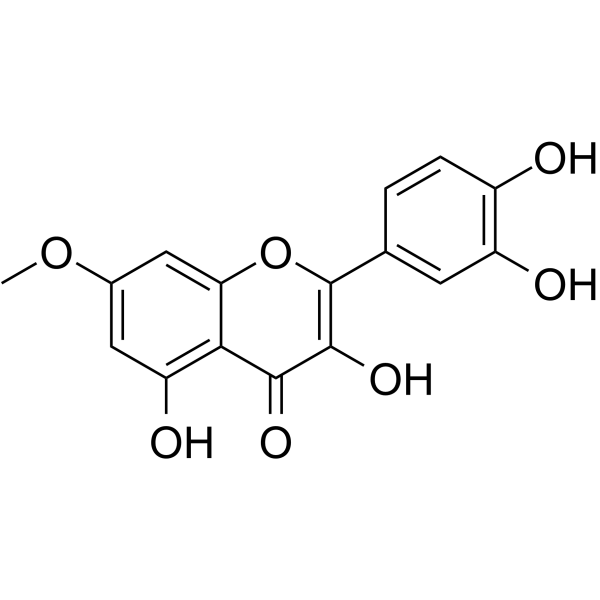
Rhamnetin
CAS No. 90-19-7
Rhamnetin( beta-Rhamnocitrin )
Catalog No. M29098 CAS No. 90-19-7
Rhamnetin, a quercetin derivative found in Coriandrum sativum, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Rhamnetin inhibits secretory phospholipase A2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 140 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 132 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 211 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 356 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 513 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 732 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRhamnetin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRhamnetin, a quercetin derivative found in Coriandrum sativum, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Rhamnetin inhibits secretory phospholipase A2.
-
DescriptionRhamnetin, a quercetin derivative found in Coriandrum sativum, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Rhamnetin inhibits secretory phospholipase A2.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonymsbeta-Rhamnocitrin
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number90-19-7
-
Formula Weight316.265
-
Molecular FormulaC16H12O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCOc1cc(O)c2c(c1)oc(-c1ccc(O)c(O)c1)c(O)c2=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Lupeolic acid
Lupeolic acid has anti-inflammatory activity.
-
Light Green SF Yello...
Light Green SF Yellowish (Acid Green 5) is an alkaline stain used for staining animal tissues and for cytoplasmic and fiber staining in plant histology.
-
Edonerpic maleate
Edonerpic maleate is a novel neurotrophic agent which can inhibit amyloid-β peptides (Aβ).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


