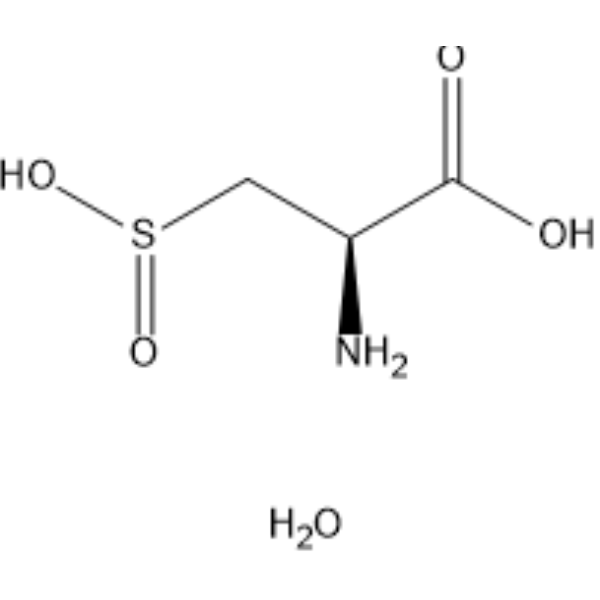
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid monohydrate
CAS No. 207121-48-0
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid monohydrate( —— )
Catalog No. M28360 CAS No. 207121-48-0
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid monohydrate is a potent agonist at rat metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 35 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 71 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 110 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 160 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Cysteinesulfinic acid monohydrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-Cysteinesulfinic acid monohydrate is a potent agonist at rat metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs).
-
DescriptionL-Cysteinesulfinic acid monohydrate is a potent agonist at rat metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) with pEC50s of 3.92, 4.6, 3.9, 2.7, 4.0, and 3.94 for mGluR1, mGluR5, mGluR2, mGluR4, mGluR6, and mGluR8, respectively.(In Vitro):L-Cysteinesulfinic acid (monohydrate) is an endogenous agonist of a metabotropic receptor coupled to stimulation of phospholipase D (PLD) activity. L-CSA (monohydrate) is an endogenous agonist of the PLD-coupled metabotropic excitatory amino acids (EAA) receptor. L-CSA (monohydrate) selectively activates the PLD-coupled receptor. 1 mM L-CSA (monohydrate) induces a significant increase in PLD activity in hippocampal slices, whereas 1 mM concentrations of L-glutamate, L-aspartate, and L-HCA are without effect. L-CSA (monohydrate) elicits a dose-dependent increase in PLD activity in rat hippocampal slices in the presence of iGluR antagonists, with an approximate EC50 of 500 uM. The PLD response induced by 1 mM L-CSA (monohydrate) is not significantly decreased in the presence of 1 uM tetrodotoxin, suggesting that this response is not dependent upon L-CSA (monohydrate)-induced increases in cell firing.
-
In VitroL-Cysteinesulfinic acid is an endogenous agonist of a metabotropic receptor coupled to stimulation of phospholipase D (PLD) activity. L-CSA is an endogenous agonist of the PLD-coupled metabotropic excitatory amino acids (EAA) receptor. L-CSA selectively activates the PLD-coupled receptor. 1 mM L-CSA induces a significant increase in PLD activity in hippocampal slices, whereas 1 mM concentrations of L-glutamate, L-aspartate, and L-HCA are without effect. L-CSA elicits a dose-dependent increase in PLD activity in rat hippocampal slices in the presence of iGluR antagonists, with an approximate EC50 of 500 uM. The PLD response induced by 1 mM L-CSA is not significantly decreased in the presence of 1 uM tetrodotoxin, suggesting that this response is not dependent upon L-CSA-induced increases in cell firing.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayNeuroscience
-
TargetGluR
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number207121-48-0
-
Formula Weight171.17
-
Molecular FormulaC3H9NO5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 41.67 mg/mL (243.44 mM)
-
SMILESO.N[C@@H](CS(O)=O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Fernandes TS, et al. Phytochemical analysis of bark from Helietta apiculata Benth and antimicrobial activities. Phytochemistry. 2017 Sep;141:131-139.
molnova catalog



related products
-
MMPIP hydrochloride
MMPIP hydrochloride is a selective antagonist of allosteric mGluR7. MMPIP hydrochloride can be used in research on the roles of mGluR7 on central nervous system functions.
-
CONIFERYL ALCOHOL
Coniferyl alcohol is a fungal growth inhibitor.
-
Epigallocatechin
(-)-Epigallocatechin is the most abundant flavonoid in green tea, can bind to unfolded native polypeptides and prevent conversion to amyloid fibrils.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


