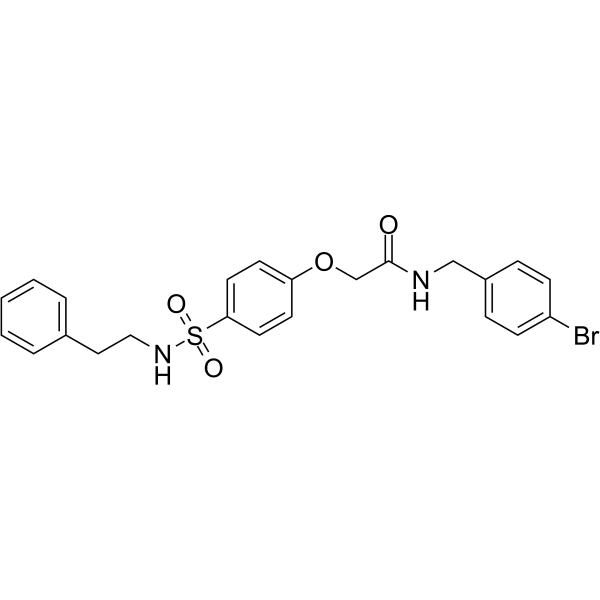
SMS1-IN-1
CAS No. 1807943-38-9
SMS1-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M26452 CAS No. 1807943-38-9
SMS1-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1, IC50 = 2.1 μM), and can be used in the atherosclerosis studies.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 186 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 155 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 217 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 353 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 547 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 807 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 1088 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSMS1-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSMS1-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1, IC50 = 2.1 μM), and can be used in the atherosclerosis studies.
-
DescriptionSMS1-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1, IC50 = 2.1 μM), and can be used in the atherosclerosis studies. (In Vitro):SMS1-IN-1 (2.5, 10 and 50 μM) shows inhibitory effect against SMS1 in a dose-dependent manner.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorD2 receptor| D3 receptor
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1807943-38-9
-
Formula Weight503.41
-
Molecular FormulaC23H23BrN2O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (496.61 mM)
-
SMILESBrc1ccc(CNC(=O)COc2ccc(cc2)S(=O)(=O)NCCc2ccccc2)cc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Holmes et al (2010) The identification of a selective DA D2 partial agonist, D3 antagonist displaying high levels of brain exposure. Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett. 20 2013
molnova catalog



related products
-
(+)-Isopulegol
(+)-Isopulegol is a monoterpenoid from Mentha canadensis L.
-
Beta-Amyloid(1-14),m...
Beta-Amyloid(1-14),mouse,rat is a 1 to 14 fragment of Amyloid-β peptide. This peptide is amino acids 1 to 14 fragment of Beta-Amyloid peptide.
-
7-ethyl-2-methylunde...
7-ethyl-2-methylundecan-4-ol is a surfactant that can be used in softeners, shampoos, soaps, detergents and other products.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


