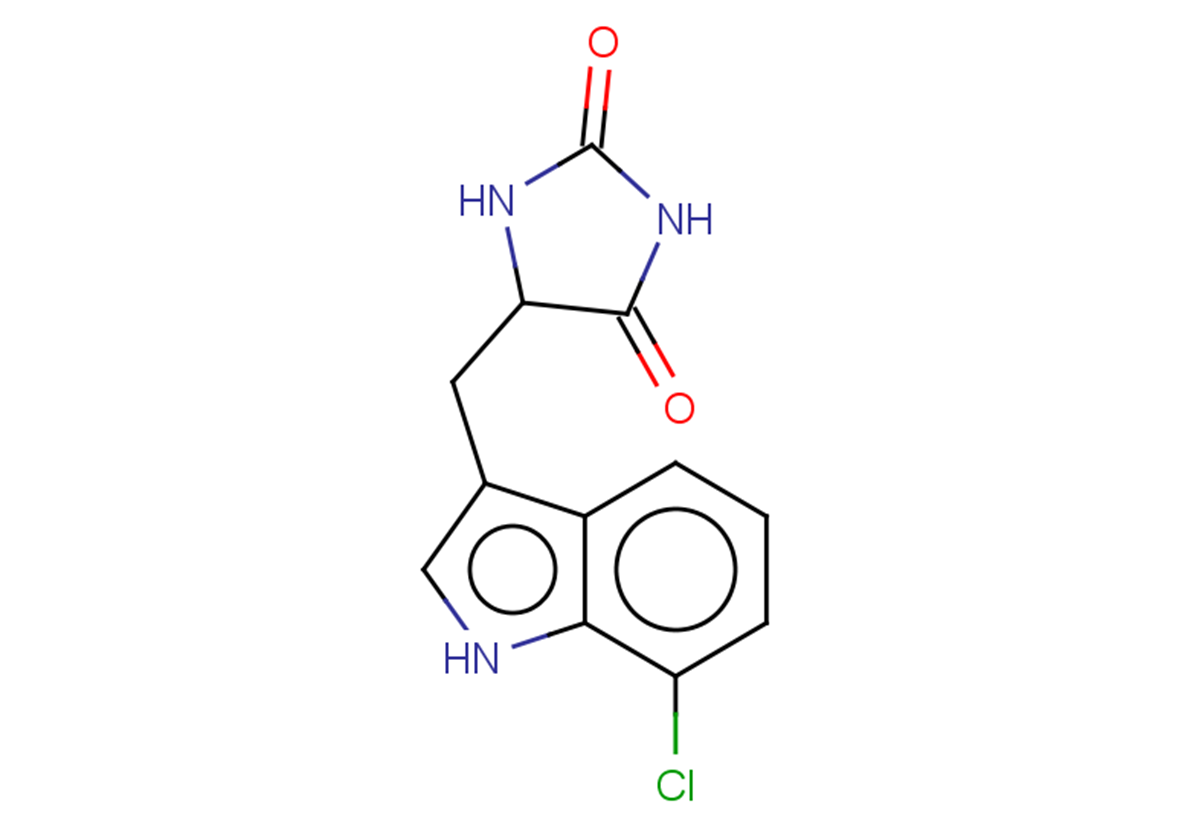
Necroptosis-IN-1
CAS No. 1391980-92-9
Necroptosis-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M23550 CAS No. 1391980-92-9
Necroptosis-IN-1 is a potent necroptosis inhibitor of RIPK1. It is an analog of Necrostatin-1.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 144 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 187 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 318 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 440 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 625 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 823 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNecroptosis-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNecroptosis-IN-1 is a potent necroptosis inhibitor of RIPK1. It is an analog of Necrostatin-1.
-
DescriptionNecroptosis-IN-1 is a potent necroptosis inhibitor of RIPK1. It is an analog of Necrostatin-1.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetRIP kinase
-
RecptorRIPK1
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1391980-92-9
-
Formula Weight263.68
-
Molecular FormulaC12H10ClN3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 249 mg/mL (944.32 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESO=C(C(Cc(c1ccc2)c[nH]c1c2Cl)N1)NC1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Jenny L Maki, et al. Fluorescence polarization assay for inhibitors of the kinase domain of receptor interacting protein 1. Anal Biochem. 2012 Aug 15;427(2):164-74.
molnova catalog



related products
-
CSLP43
CSLP43 (RIPK2 inhibitor CSLP43) is a novel potent, ATP pocket-binding RIPK2 inhibitor with IC50 of 19.9 nM in ADPGlo assay.
-
RIPK2 inhibitor OD36
RIPK2 inhibitor OD36 is a potent, specific, ATP-competitive inhibitor of RIPK2 with IC50 of 5.3 nM.
-
Cpd27
Cpd27 (TIE-2/VEGFR-2 kinase-IN-2) is a TIE-2 and VEGFR-2 inhibitor that inhibits RIPK1 and protects RGCs from TNF-stimulated cell death and can be used to study glaucoma.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


