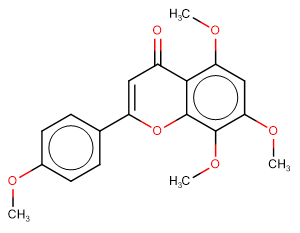
6-Demethoxytangeretin
CAS No. 6601-66-7
6-Demethoxytangeretin( —— )
Catalog No. M21526 CAS No. 6601-66-7
6-Demethoxytangeretin is a citrus flavonoid isolated from Citrus depressa.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 121 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 188 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 330 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 479 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 682 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name6-Demethoxytangeretin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description6-Demethoxytangeretin is a citrus flavonoid isolated from Citrus depressa.
-
Description6-Demethoxytangeretin is a citrus flavonoid isolated from Citrus depressa.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetALK
-
RecptorALK| MAPK
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6601-66-7
-
Formula Weight342.3
-
Molecular FormulaC19H18O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 12.5 mg/mL (36.51 mM)
-
SMILESCOc(cc1)ccc1C(Oc1c2c(OC)cc(OC)c1OC)=CC2=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kim YM et al. A citrus flavonoid 6-demethoxytangeretin suppresses production and gene expression of interleukin-6 in human mast cell-1 via anaplastic lymphoma kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(5):871-6. Epub 2014 Feb 5.
molnova catalog



related products
-
CPI-169
CPI-169 is a potent, and selective EZH2 inhibitor with IC50 of 0.24 nM, 0.51 nM, and 6.1 nM for EZH2 WT, EZH2 Y641N, and EZH1, respectively.
-
KER047
KER047 (ALK2-IN-4) is an ALK2 inhibitor with potential anticancer activity and can be used in the study of non-small cell lung cancer.
-
Tyrphostin AG 879
Tyrphostin AG 879 effectively inhibits HER2/ErbB2 (IC50: 1 μM), 100- and 500-fold higher selective to ErbB2 than EGFR and PDGFR.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


