Bornyl acetate(b)
CAS No. 20347-65-3
Bornyl acetate(b)( (+)-Bornyl acetate )
Catalog No. M21492 CAS No. 20347-65-3
(+)-Bornyl acetate has a stronger inhibitory effect on root growth of Arabidopsis seedlings.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 91 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 141 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBornyl acetate(b)
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description(+)-Bornyl acetate has a stronger inhibitory effect on root growth of Arabidopsis seedlings.
-
Description(+)-Bornyl acetate has a stronger inhibitory effect on root growth of Arabidopsis seedlings.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(+)-Bornyl acetate
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number20347-65-3
-
Formula Weight196.29
-
Molecular FormulaC12H20O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
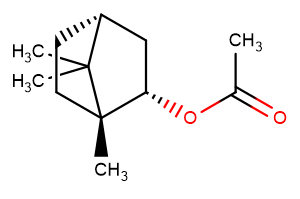
SMILESCC(C)([C@H](CC1)C2)[C@]1(C)[C@H]2OC(C)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Jun-Ichiro Horiuchi et al. Exposing Arabidopsis seedlings to borneol and bornyl acetate affects root growth: Specificity due to the chemical and optical structures of the compounds. Journal of Plant Interactions. 17 Sep 2007. Volume 2 Issue 2: 101-104.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(Val3)-β-Casomorphin...
(Val3)-β-Casomorphin (1-4) amide (bovine)
-
BDP-13176
BDP-13176 is a potent?inhibitor of fascin 1(Kd?of 90 nM and an?IC50?of 240 nM). It has potential as an anti-metastatic agent.
-
Adrenomedullin (1-12...
Adrenomedullin (1-12), human



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


