Vanin-1-IN-1
CAS No. 2173134-00-2
Vanin-1-IN-1( VUN34002? )
Catalog No. M21182 CAS No. 2173134-00-2
Vanin-1-IN-1 is an vanin-1 enzyme inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 74 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 135 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 193 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 305 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 458 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameVanin-1-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionVanin-1-IN-1 is an vanin-1 enzyme inhibitor.
-
DescriptionVanin-1-IN-1 is an vanin-1 enzyme inhibitor.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsVUN34002?
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorvanin
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2173134-00-2
-
Formula Weight354.4
-
Molecular FormulaC18H22N6O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:125 mg/mL (352.70 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
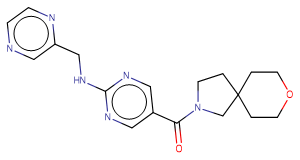
SMILESO=C(c1cnc(NCc2cnccn2)nc1)N1CCC2(CCOCC2)C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Agustin Casimiro-Garcia et al. Novel pyrimidine carboxamides as inhibitors of vanin-1 enzyme. WO2018011681A1.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Cyanosafracin B
Cyanosafracin B is a compound which can be used in the synthesis of ecteinascidin ET-743 (an antitumor chemotherapy drug).
-
Flecainide hydrochlo...
Flecainide is a medication used to prevent and treat abnormally fast heart rates.?This includes ventricular and supraventricular tachycardias.
-
3-(Methylthio)propio...
3-methylthiopropionate is one of the metabolites of methionine (especially of D-methionine). Cultures of Streptomyces lincolnensis accumulated 3-methylthioacrylic acid in amounts directly related to the concentration of methionine in the medium. The first intermediate in the pathway may be the keto acid which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to 3-methylthiopropionic acid.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


