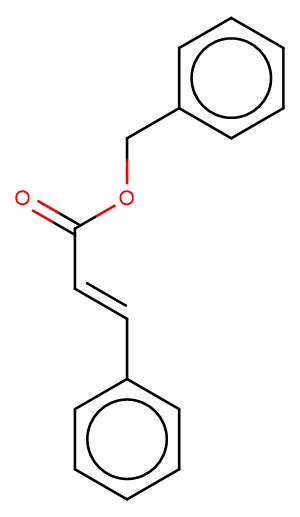
Benzyl cinnamate
CAS No. 103-41-3
Benzyl cinnamate( Cinnamein | ?Benzylcinnamoate | Benzyl 3-phenylpropenoate | Cinnamic acid benzyl ester )
Catalog No. M21171 CAS No. 103-41-3
Benzyl cinnamate is a natural product isolated from various plant specieswith anti-inflammatory activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 33 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 41 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBenzyl cinnamate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBenzyl cinnamate is a natural product isolated from various plant specieswith anti-inflammatory activity.
-
DescriptionBenzyl cinnamate is a natural product isolated from various plant specieswith anti-inflammatory activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsCinnamein | ?Benzylcinnamoate | Benzyl 3-phenylpropenoate | Cinnamic acid benzyl ester
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorImmunology & Inflammation related
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number103-41-3
-
Formula Weight238.28
-
Molecular FormulaC16H14O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:47 mg/mL (197.24 mM)
-
SMILESO=C(/C=C/c1ccccc1)OCc1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Bhatia SP et al. Fragrance material review on benzyl cinnamate. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45 Suppl 1:S40-8. Epub 2007 Sep 14.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nortrachelogenin
Nortrachelogenin ((-)-Wikstromol), which can be extracted from Partrinia scabiosaefolia, has antifungal activity and induces membrane disruption and cysteinyl asparagin-dependent apoptosis.
-
BISMUTH SUBGALLATE
Bismuth subgallate is an astringent and antiseptic and is applied to skin diseases such as eczema.
-
(+)-Catechin Hydrate
(+)-Catechin Hydrate is an antioxidant flavonoid of plant origin; a free radical scavenger, preventing free radical-mediated damage in a variety of biological systems.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


