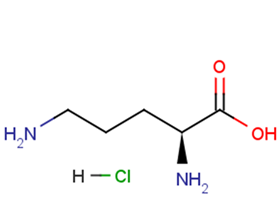
L(+)-Ornithine hydrochloride
CAS No. 3184-13-2
L(+)-Ornithine hydrochloride( —— )
Catalog No. M18420 CAS No. 3184-13-2
L-ornithine hydrochloride has an antifatigue effect by increasing the efficiency of energy consumption and promoting the excretion of ammonia. It is one of the key reactants in the urea cycle.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 60 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 86 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL(+)-Ornithine hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-ornithine hydrochloride has an antifatigue effect by increasing the efficiency of energy consumption and promoting the excretion of ammonia. It is one of the key reactants in the urea cycle.
-
DescriptionL-ornithine hydrochloride has an antifatigue effect by increasing the efficiency of energy consumption and promoting the excretion of ammonia. It is one of the key reactants in the urea cycle.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3184-13-2
-
Formula Weight168.62
-
Molecular FormulaC5H13ClN2O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 50 mg/mL (296.52 mM)
-
SMILESC(CC(C(=O)O)N)CN.Cl
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Z-Phe-Ala-NH2
Heterocyclic Organic Compound
-
Senkyunolide N
Senkyunolide N exhibits prostaglandin H endoperoxide synthase-I (COX-I) and endoperoxide synthase-II (COX-II)) Inhibitory activity at pH 7 and at a concentration of 250 pg ml(-1) .
-
(2E,4E)-2,4-Decadien...
(2E,4E)-Decadienoic acid is an anti-oomycete aliphatic compound that can be found in Coculture of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma asperellum.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


