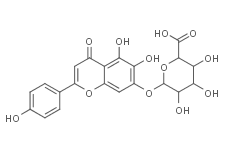
Scutellarin
CAS No. 27740-01-8
Scutellarin( —— )
Catalog No. M18352 CAS No. 27740-01-8
Scutellarin, an active flavone isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis, can inhibit RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoclasts, and down-regulate the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling in HCC cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 44 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 144 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 351 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameScutellarin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionScutellarin, an active flavone isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis, can inhibit RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoclasts, and down-regulate the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling in HCC cells.
-
DescriptionScutellarin, an active flavone isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis, can inhibit RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoclasts, and down-regulate the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling in HCC cells.(In Vitro):Scutellarin treatment significantly reduces HepG2 cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, and inhibits migration and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. Scutellarin treatment significantly reduces STAT3 and Girders of actin filaments (Girdin) expression, STAT3 and Akt phosphorylation in HCC cells. Introduction of STAT3 overexpression restores the scutellarin-downregulated Girdin expression, Akt activation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Furthermore, induction of Girdin overexpression completely abrogates the inhibition of scutellarin on the Akt phosphorylation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Scutellarin can inhibit HCC cell metastasis in vivo, and migration and invasion in vitro by down-regulating the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling. Scutellarin selectively enhances Akt phosphorylation. Scutellarin is a putative therapeutic agent as it has been found to not only suppress microglial activation thus ameliorating neuroinflammation, but also enhance astrocytic reaction. Acutellarin amplifies the astrocytic reaction by upregulating the expression of neurotrophic factors among others thus indicating its neuroprotective role. Remarkably, the effects of scutellarin on reactive astrocytes are mediated by activated microglia supporting a functional "cross-talk" between the two glial types. Scutellarin can suppress RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis, the function of osteoclast bone resorption, and the expression levels of osteoclast-specific genes (tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), cathepsin K, c-Fos, NFATc1). Further investigation indicates that Scutellarin can inhibit RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway, including JNK1/2, p38, ERK1/2, and IκBα phosphorylation.(In Vivo):Scutellarin (50 mg/kg/day) significantly mitigates the lung and intrahepatic metastasis of HCC tumors in vivo. The numbers of the lung and intrahepatic metastatic tumors in the scutellarin-treated group are significantly less than that in the controls. The rats treated with Scutellarin display a significant alleviation in neurobehavioral deficits compared to the SAH group. Scutellarin enhanced eNOS expression compared with SAH rats.
-
In VitroScutellarin treatment significantly reduces HepG2 cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, and inhibits migration and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. Scutellarin treatment significantly reduces STAT3 and Girders of actin filaments (Girdin) expression, STAT3 and Akt phosphorylation in HCC cells. Introduction of STAT3 overexpression restores the scutellarin-downregulated Girdin expression, Akt activation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Furthermore, induction of Girdin overexpression completely abrogates the inhibition of scutellarin on the Akt phosphorylation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Scutellarin can inhibit HCC cell metastasis in vivo, and migration and invasion in vitro by down-regulating the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling. Scutellarin selectively enhances Akt phosphorylation. Scutellarin is a putative therapeutic agent as it has been found to not only suppress microglial activation thus ameliorating neuroinflammation, but also enhance astrocytic reaction. Acutellarin amplifies the astrocytic reaction by upregulating the expression of neurotrophic factors among others thus indicating its neuroprotective role. Remarkably, the effects of scutellarin on reactive astrocytes are mediated by activated microglia supporting a functional "cross-talk" between the two glial types. Scutellarin can suppress RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis, the function of osteoclast bone resorption, and the expression levels of osteoclast-specific genes (tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), cathepsin K, c-Fos, NFATc1). Further investigation indicates that Scutellarin can inhibit RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway, including JNK1/2, p38, ERK1/2, and IκBα phosphorylation.
-
In VivoScutellarin (50 mg/kg/day) significantly mitigates the lung and intrahepatic metastasis of HCC tumors in vivo. The numbers of the lung and intrahepatic metastatic tumors in the scutellarin-treated group are significantly less than that in the controls. The rats treated with Scutellarin display a significant alleviation in neurobehavioral deficits compared to the SAH group. Scutellarin enhanced eNOS expression compared with SAH rats.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetAntioxidant
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number27740-01-8
-
Formula Weight462.37
-
Molecular FormulaC21H18O12
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL; 216.28 mM
-
SMILESc1cc(ccc1c1cc(=O)c2c(c(c(cc2o1)O[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O1)C(=O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Wang WW, et al. J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Oct 29.
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Chlorophenylhydraz...
4-Chlorophenylhydrazine?hydrochloride?is?used?as?a?pharmaceutical?intermediate.
-
Diformylphloroglucin...
Diformylphloroglucinol (2,4,6-Trihydroxyisophthalaldehyde) is an acyl resorcinol isolated from the leaves of the Eucalyptus nigra tree and is a raw material for the synthesis of resorcinol compounds with antioxidant and antiulcer activity.
-
Mildronate dihydrate
Mildronate dihydrate is an inhibitor of biosynthesis of L-carnitine by gamma-butyrobetaine (GBB) hydroxylase and as a competitive inhibitor of renal carnitine reabsorption.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


