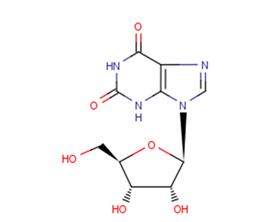
Xanthosine
CAS No. 146-80-5
Xanthosine( Xanthosine | NSC 18930 | NSC-18930 )
Catalog No. M18039 CAS No. 146-80-5
Xanthosine is produced by guanine-free mutants of bacteria e. g. Bacillus subtilis, Aerobacter aerogenes.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 44 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameXanthosine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionXanthosine is produced by guanine-free mutants of bacteria e. g. Bacillus subtilis, Aerobacter aerogenes.
-
DescriptionXanthosine treatment has been demonstrated to promote expansion of putative mammary stem cells. Xanthosine treatment also increased the proliferation rate of bovine MEC in vitro
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsXanthosine | NSC 18930 | NSC-18930
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number146-80-5
-
Formula Weight284.22
-
Molecular FormulaC10H12N4O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 33.33 mg/mL 117.26 mM;
-
SMILESC1=NC2=C(N1C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)NC(=O)NC2=O
-
Chemical Name9-beta-D-Ribofuranosylxanthine
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Sibirioside A
Sibirioside A is a phenylpropanoid glycoside isolated fromScrophulariae Radix.Sibirioside A has the potential for the treatment of diabetes.
-
DAPI Dihydrochloride
DAPI Dihydrochloride is a cell-permeable fluorescent probe by binding in the minor grove of A-T rich sequences of DNA, used to stain DNA and chromosomes, with a preference for adenine and thymine rich DNA.
-
Cyclic AMP
Adenosine cyclophosphate combined with vitamin C treatment of children with viral myocarditis has exact curative effect, and it can improve cardiac function of patients and improve immune function.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


