 Home -
Products -
Cell Cycle/DNA Damage -
HDAC -
4-(1H-Pyrazol-4-yl)-7-((2-(trimethylsilyl)ethoxy)-methyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine
Home -
Products -
Cell Cycle/DNA Damage -
HDAC -
4-(1H-Pyrazol-4-yl)-7-((2-(trimethylsilyl)ethoxy)-methyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine
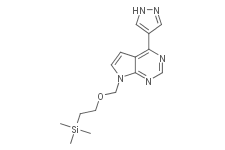
4-(1H-Pyrazol-4-yl)-7-((2-(trimethylsilyl)ethoxy)-methyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine
CAS No. 941685-27-4
4-(1H-Pyrazol-4-yl)-7-((2-(trimethylsilyl)ethoxy)-methyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine( —— )
Catalog No. M17678 CAS No. 941685-27-4
Detail unknown.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-(1H-Pyrazol-4-yl)-7-((2-(trimethylsilyl)ethoxy)-methyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDetail unknown.
-
DescriptionDetail unknown.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetHDAC
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number941685-27-4
-
Formula Weight315.45
-
Molecular FormulaC15H21N5OSi
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (317.01 mM)
-
SMILESC[Si](C)(C)CCOCn1ccc2c(ncnc12)c1c[nH]nc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
CRA-026440
CRA-026440(PCI-34051) is a highly potent HDAC inhibitor with inhibitory effects on HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC6, HDAC8 and HDAC10 with Ki values of 4,14,11,15,7 and 20 nM, respectively.
-
Class I and IIB HDAC...
Class I and IIB HDAC inhibitor 42 is a novel potent, selective class I and IIB inhibitor.
-
Crebinostat
Crebinostat is a novel cognitive enhancer that inhibits class I HDAC/1/2/3.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com

