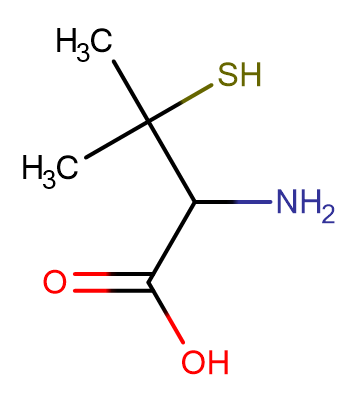
DL-Penicillamine
CAS No. 52-66-4
DL-Penicillamine( —— )
Catalog No. M14864 CAS No. 52-66-4
The most characteristic degradation product of the penicillin antibiotics. It is used as an antirheumatic and as a chelating agent in Wilson's disease.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 72 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 110 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 129 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDL-Penicillamine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThe most characteristic degradation product of the penicillin antibiotics. It is used as an antirheumatic and as a chelating agent in Wilson's disease.
-
DescriptionThe most characteristic degradation product of the penicillin antibiotics. It is used as an antirheumatic and as a chelating agent in Wilson's disease. (In Vivo):DL-Penicillamine (25 mg/kg; i.p.; twice daily, for 5 days) has antidotal effects in thallotoxicosis rats when co-treated with Prussian blue (HY-106594A).
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoDL-Penicillamine (25 mg/kg; i.p.; twice daily, for 5 days) has antidotal effects in thallotoxicosis rats when co-treated with Prussian blue (HY-106594A). Animal Model:Male Wistar rats, NIH strain (intoxicated by i.p. injection of 32 mg/kg thallium (I) acetate)Dosage:25 mg/kg Administration:i.p.; twice daily, for 5 daysResult:Decreased slightly the thallium content in blood, organs and brain.Increased the probability survival when co-treated with Prussian blue (50 mg/kg; p.o.).
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number52-66-4
-
Formula Weight149.21
-
Molecular FormulaC5H11NO2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityFree soluble in Water
-
SMILESCC(C)(S)C(N)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Brewer GJ. Expert Opin PharmacOthers. 2006, 7(3):317-24
molnova catalog



related products
-
Benzoylalbiflorin
Benzoylalbiflorin is a monoterpenoid isolated from Radix Paeoniae Alba.
-
14-Deoxyandrographol...
14-Deoxyandrographolide is a bioactive compound of Andrographis paniculata with hepatoprotective efficacy. It desensitizes hepatocytes to TNF-α-mediated apoptosis through the release of TNFRSF1A release.
-
Neomangiferin
Neomangiferin has beneficial effects on high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


