BML-277
CAS No. 516480-79-8
BML-277( BML-277 | C 3742 | Checkpoint Kinase 2 Inhibitor II )
Catalog No. M14798 CAS No. 516480-79-8
BML-277 (C 3742) is a selective Chk2 (checkpoint kinase 2) inhibitor with an IC50 of 15 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 73 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 151 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 259 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 368 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 538 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBML-277
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBML-277 (C 3742) is a selective Chk2 (checkpoint kinase 2) inhibitor with an IC50 of 15 nM.
-
DescriptionBML-277 (C 3742) is a selective Chk2 (checkpoint kinase 2) inhibitor with an IC50 of 15 nM.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBML-277 | C 3742 | Checkpoint Kinase 2 Inhibitor II
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetChk
-
RecptorChk2
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number516480-79-8
-
Formula Weight363.8
-
Molecular FormulaC20H14ClN3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
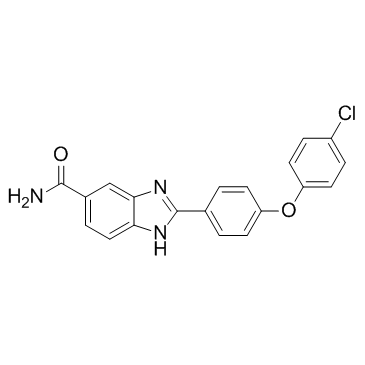
SMILESO=C(C1=CC=C2C(N=C(C3=CC=C(OC4=CC=C(Cl)C=C4)C=C3)N2)=C1)N
-
Chemical Name2-(4-(4-Chlorophenoxy)phenyl)-1H-benzimidazole-5-carboxamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
AZD-7762
AZD-7762 (AZD7762) is a?potent and selective inhibitor of Chk1/2 with IC50 of 5 nM.
-
CCT-245737
A highly potent, selective, ATP-competitive inhibitor of Chk1 with IC50 of 1.3 nM; weak inhibition on Chk2 (IC50=2440 nM).
-
SAR-020106
SAR-020106 is a potent, ATP-competitive, and selective CHK1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 13.3 nmol/L on the isolated human enzyme.SAR-020106 is an ATP-competitive, potent, and selective CHK1 inhibitor with an IC(50) of 13.3 nmol/L on the isolated human enzyme. This compound abrogates an etoposide-induced G(2) arrest with an IC(50) of 55 nmol/L in HT29 cells, and significantly enhances the cell killing of gemcitabine and SN38 by 3.0- to 29-fold in several colon tumor lines in vitro and in a p53-dependent fashion.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


