Thiomyristoyl
CAS No. 1429749-41-6
Thiomyristoyl( Thiomyristoyl )
Catalog No. M11816 CAS No. 1429749-41-6
Thiomyristoyl is a highly selective and potent SIRT2 inhibitor with IC50 of 28 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 120 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 84 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 120 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 227 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 373 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 555 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameThiomyristoyl
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThiomyristoyl is a highly selective and potent SIRT2 inhibitor with IC50 of 28 nM.
-
DescriptionThiomyristoyl is a highly selective and potent SIRT2 inhibitor with IC50 of 28 nM, displays no significant activity against SIRT1/3/5/6/7 (Ic50>100 uM); promotes c-Myc ubiquitination and degradation, exhibits broad anticancer effect in various human cancer cells while having limited effects on non-cancerous cells; demonstrates in vivo effect in mouse models of breast cancer.(In Vitro):Thiomyristoyl (TM) is a potent SIRT2-specific inhibitor with broad anticancer activity but little effect on non-cancerous cells. SIRT2-inhibition promotes c-Myc ubiquitination and degradation, suggesting the therapeutic potential of TM to target certain c-Myc-driven cancers. TM could inhibit SIRT2 with an IC50 of 28 nM, but inhibits SIRT1 with an IC50 value of 98 μM and does not inhibit SIRT3 even at 200 μM. TM inhibits three human breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7, MDA-MB-468, and MDA-MB-231.(In Vivo):TM inhibits tumor growth in mouse models of breast cancer. TM does not cause significant toxicity in mice and no significant weight loss is observed in TM-treated mice. S5H, the acetyl-a-tubulin level is moderately but statistically significantly increased in tumors from TM-treated mice compared with those from vehicle-treated mice, suggesting that TM indeed inhibits SIRT2 in vivo.
-
In VitroThiomyristoyl (TM) is a potent SIRT2-specific inhibitor with broad anticancer activity but little effect on non-cancerous cells. SIRT2-inhibition promotes c-Myc ubiquitination and degradation, suggesting the therapeutic potential of TM to target certain c-Myc-driven cancers. TM could inhibit SIRT2 with an IC50 of 28 nM, but inhibits SIRT1 with an IC50 value of 98 μM and does not inhibit SIRT3 even at 200 μM. TM inhibits three human breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7, MDA-MB-468, and MDA-MB-231.
-
In VivoTM inhibits tumor growth in mouse models of breast cancer. TM does not cause significant toxicity in mice and no significant weight loss is observed in TM-treated mice. S5H, the acetyl-a-tubulin level is moderately but statistically significantly increased in tumors from TM-treated mice compared with those from vehicle-treated mice, suggesting that TM indeed inhibits SIRT2 in vivo.
-
SynonymsThiomyristoyl
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetSirtuin
-
RecptorSIRT1|SIRT2
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1429749-41-6
-
Formula Weight581.85204
-
Molecular FormulaC34H51N3O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 32 mg/mL
-
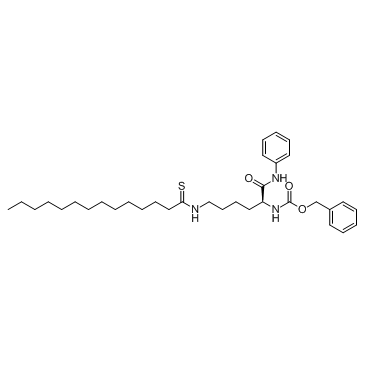
SMILESO=C(OCC1=CC=CC=C1)N[C@@H](CCCCNC(CCCCCCCCCCCCC)=S)C(NC2=CC=CC=C2)=O
-
Chemical NameCarbamic acid, N-[(1S)-1-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-5-[(1-thioxotetradecyl)amino]pentyl]-, phenylmethyl ester
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Teng YB, et al. Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 23;5:8529.
2. Jing H, et al. Cancer Cell. 2016 Mar 14;29(3):297-310.
3. Wang Y, et al. Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Mar 16;24(3):339-345.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SRT 2183
SRT 2183 is a potent, selective SIRT1 activator with EC1.5 of 0.36 uM.
-
Neodiosmin
Neodiosmin has poor aqueous solubility but exerts a good debittering effect and is a strong antioxidant with potential applications in foods, beverages, and pharmaceutical preparations.
-
Pristimerin
Pristimerin has anticancer activity, treatment with Pristimerin may be a potential strategy for the suppression of hypoxia-induced metastasis through the reversal of hypoxia-induced stem cell characteristics and EMT in cancer cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


