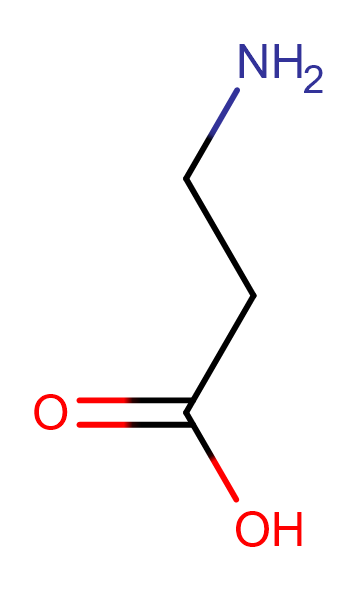
beta-Alanine
CAS No. 107-95-9
beta-Alanine( —— )
Catalog No. M10320 CAS No. 107-95-9
An amino acid formed in vivo by the degradation of dihydrouracil and carnosine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namebeta-Alanine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAn amino acid formed in vivo by the degradation of dihydrouracil and carnosine.
-
DescriptionAn amino acid formed in vivo by the degradation of dihydrouracil and carnosine. Since neuronal uptake and neuronal receptor sensitivity to beta-alanine have been demonstrated, the compound may be a false transmitter replacing GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID. A rare genetic disorder, hyper-beta-alaninemia, has been reported.(In Vitro):Cells treated with β-alanine display significantly suppressed basal and peak ECAR (aerobic glycolysis), with simultaneous increase in glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1). Additionally, cells treated with β-alanine exhibit significantly reduced basal and peak OCR (oxidative metabolism), which is accompanied by reduction in mitochondrial content with subsequent suppression of genes which promote mitochondrial biosynthesis. Suppression of glycolytic and oxidative metabolism by β-alanine results in the reduction of total metabolic rate, although cell viability is not affected.β-alanine is shown to reduce both cell migration and proliferation without acting in a cytotoxic fashion. Moreover, β-alanine significantly increases malignant cell sensitivity to doxorubicin, suggesting a potential role as a co-therapeutic agent.
-
In VitroCells treated with β-alanine display significantly suppressed basal and peak ECAR (aerobic glycolysis), with simultaneous increase in glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1). Additionally, cells treated with β-alanine exhibit significantly reduced basal and peak OCR (oxidative metabolism), which is accompanied by reduction in mitochondrial content with subsequent suppression of genes which promote mitochondrial biosynthesis. Suppression of glycolytic and oxidative metabolism by β-alanine results in the reduction of total metabolic rate, although cell viability is not affected.β-alanine is shown to reduce both cell migration and proliferation without acting in a cytotoxic fashion. Moreover, β-alanine significantly increases malignant cell sensitivity to doxorubicin, suggesting a potential role as a co-therapeutic agent.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetAmino Acids and Derivatives
-
RecptorAmino Acids and Derivatives
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number107-95-9
-
Formula Weight89.09
-
Molecular FormulaC3H7NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Water
-
SMILESNCCC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Hill CA, et al. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Fmoc-L-Proline
Fmoc-L-Proline (Fmoc-Pro-OH) is a proline derivative.
-
L-Ornithine
L-ornithine has an antifatigue effect in increasing the efficiency of energy consumption and promoting the excretion of ammonia.
-
DL-Glutamine
A non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and is involved in many metabolic processes.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


