Laetrile
CAS No. 29883-15-6
Laetrile( (–)-Amygdalin | (D)-Amygdalin | (R)-Amygdalin | Amygdaloside | NSC 15780 )
Catalog No. M13919 CAS No. 29883-15-6
Laetrile is a glycoside initially isolated from the seeds of the tree Prunus dulcis, also known as bitter almonds.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 38 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 49 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLaetrile
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLaetrile is a glycoside initially isolated from the seeds of the tree Prunus dulcis, also known as bitter almonds.
-
DescriptionLaetrile is a glycoside initially isolated from the seeds of the tree Prunus dulcis, also known as bitter almonds.(In Vitro):Amygdalin has antitumor activity. Some advances had been made on the antitumor mechanism of amygdalin. Amygdalin downregulates especially genes belonging to cell cycle category: exonuclease 1, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family F, member 2, MRE11 meiotic recombination 11 homolog A, topoisomerase (DNA) I, and FK506 binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1. RT-PCR analysis reveals that mRNA levels of these genes are also decreased by amygdalin treatment in SNU-C4 human colon cancer cells.(In Vivo):Amygdalin is effective at alleviating inflammatory pain and that it can be used as an analgesic with anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities. The intramuscular injection of amygdalin significantly reduced the formalin-induced tonic pain in both early (the initial 10 min after formalin injection) and late phases (10-30 min following the initial formalin injection). During the late phase, amygdalin reduces the formalin-induced pain in a dose-dependent manner in a dose range less than 1 mg/kg.
-
In VitroAmygdalin has antitumor activity. Some advances had been made on the antitumor mechanism of amygdalin. Amygdalin downregulates especially genes belonging to cell cycle category: exonuclease 1, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family F, member 2, MRE11 meiotic recombination 11 homolog A, topoisomerase (DNA) I, and FK506 binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1. RT-PCR analysis reveals that mRNA levels of these genes are also decreased by amygdalin treatment in SNU-C4 human colon cancer cells.
-
In VivoAmygdalin is effective at alleviating inflammatory pain and that it can be used as an analgesic with anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities. The intramuscular injection of amygdalin significantly reduced the formalin-induced tonic pain in both early (the initial 10 min after formalin injection) and late phases (10-30 min following the initial formalin injection). During the late phase, amygdalin reduces the formalin-induced pain in a dose-dependentmanner in a dose range less than 1 mg/kg.
-
Synonyms(–)-Amygdalin | (D)-Amygdalin | (R)-Amygdalin | Amygdaloside | NSC 15780
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number29883-15-6
-
Formula Weight457.43
-
Molecular FormulaC20H27NO11
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 91 mg/mL (198.93 mM)
-
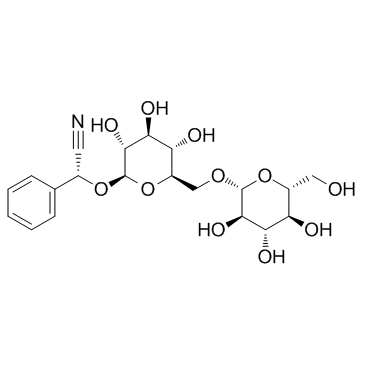
SMILESN#CC(O[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O2)O)O)O)O1)O)O)O)C3=CC=CC=C3
-
Chemical Name[(6-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy](phenyl)acetonitrile
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
PIN1 inhibitor API-1
PIN1 inhibitor API-1 is a specific Pin1 inhibitor (IC50: 72.3 nM). PIN1 inhibitor API-1 retains the active conformation of pXPO5 and restores the ability of pXPO5 to transport pre-miRNAs from the nucleus to cytoplasm, thus up-regulating the anticancer miRNA biogenesis to suppress both in vitro and in vivo hepatocellular carcinoma development.
-
Xenopsin 2TFA(51827-...
Xenopsin(2TFA) is a neurotensin-like octapeptide?previously isolated from amphibian skin.The octapeptide xenopsin, previously isolated from amphibian skin, stimulates exocrine pancreatic secretion of bicarbonate and protein in conscious dogs and increases the volume of secretion.
-
Tubulin inhibitor 11
Tubulin Inhibitor 11 is a potent, orally active agent that inhibits tubulin by targeting the Colchicine binding site. It impedes tubulin polymerization, leading to mitotic blockade and apoptosis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


