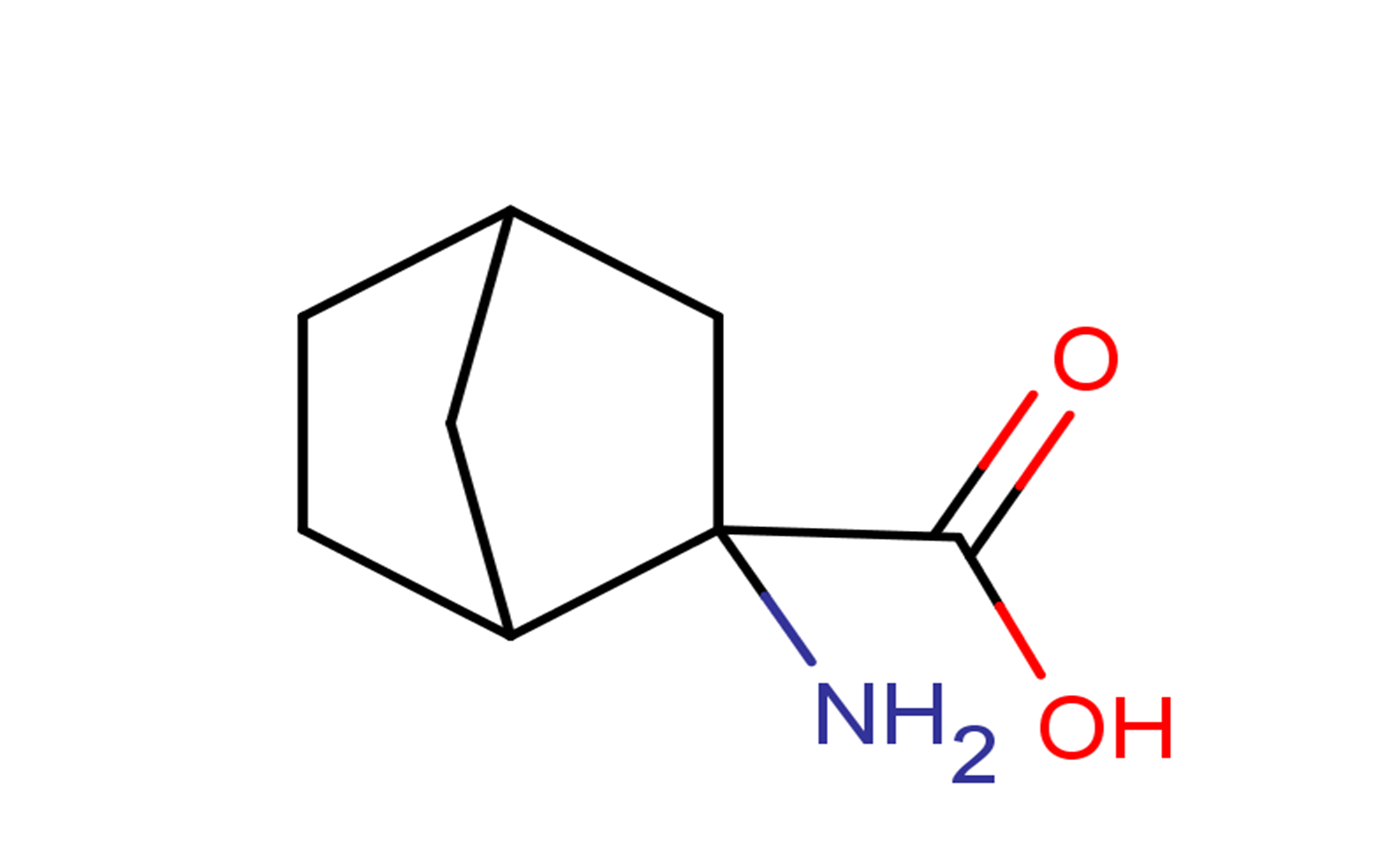
LAT1-IN-1
CAS No. 20448-79-7
LAT1-IN-1( BCH )
Catalog No. M23915 CAS No. 20448-79-7
LAT1-IN-1 (BCH) ?significantly inhibit cellular uptake of amino acids and mTOR phosphorylation, which induces the suppression of cancer growth and apoptosis.?
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 82 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLAT1-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLAT1-IN-1 (BCH) ?significantly inhibit cellular uptake of amino acids and mTOR phosphorylation, which induces the suppression of cancer growth and apoptosis.?
-
DescriptionLAT1-IN-1 (BCH) ?significantly inhibit cellular uptake of amino acids and mTOR phosphorylation, which induces the suppression of cancer growth and apoptosis.?is a selective and competitive inhibitor of large neutral amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1).
-
In VitroBCH (1-100 mM; 3 days; KYSE30 and KYSE150 esophageal cancer cells) treatment suppresses cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner.BCH (30 mM; 24 and 48 hours; KYSE30 and KYSE150 cells) treatment significantly increases cell population in the G0/G1 phase in both KYSE30 and KYSE150 cells, indicating that BCH induces cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. BCH (30 mM; 0-24 hours; KYSE30 and KYSE150 cells) treatment decreases phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and p70S6K at 30 minutes and the decrease is continued for 24 hours. The amount of mTOR, 4E-BP1, and p70S6K proteins is slightly decreased. Cell Proliferation Assay Cell Line: KYSE30 and KYSE150 esophageal cancer cells Concentration:1 mM, 3 mM, 5 mM, 10 mM, 20 mM, 30 mM, 40 mM, 50 mM, or 100 mM Incubation Time:3 daysResult:Cell proliferation was suppressed in a dose-dependent manner. Cell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:KYSE30 and KYSE150 cells Concentration:30 mM Incubation Time:24 and 48 hours Result:Cell cycle arrest.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:KYSE30 and KYSE150 cells Concentration:30 mM Incubation Time:0 hour, 0.5 hour, 1 hour, 3 hours, 6 hours, 24 hours Result: Phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and p70S6K was decreased. The amount of mTOR, 4E-BP1, and p70S6K proteins was slightly decreased.
-
In VivoBCH (200 mg/kg; intravenous injection; daily; for 14 days; male BALB/c nude mice) treatment significantly delays tumor growth and decreases glucose metabolism, indicating that LAT1 inhibition potentially suppresses esophageal cancer growth in vivo. Animal Model:Male BALB/c nude mice (5-week-old) with KYSE150 cells Dosage:200 mg/kg Administration:Intravenous injection; daily; for 14 days Result:Significantly delayed tumor growth and decreased glucose metabolism.
-
SynonymsBCH
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorLAT1|Apoptosis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number20448-79-7
-
Formula Weight155.19
-
Molecular FormulaC8H13NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O:12.5 mg/mL (80.55 mM; Need ultrasonic);DMSO:< 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
-
SMILESC1CC2CC1CC2(C(=O)O)N
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Ohshima Y, et al. Efficacy of system l amino acid transporter 1 inhibition as a therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2016 Oct;107(10):1499-1505.
molnova catalog



related products
-
DT2216
DT2216 inhibits various Bcl-XL-dependent leukemias and cancer cells, but is significantly less toxic to platelets.DT2216 is a selective B-cell lymphoma, extremely large (BCL-XL), proteolytic targeting chimera (PROTAC).
-
NM-3
NM-3 is an orally available anti-angiogenic inhibitor with anti-tumour activity.NM-3 is used as a radiation modulator in vitro and in vivo.
-
Hinokitiol
Hinokitiol (4-Isopropyltropolone;β-Thujaplicin) is a tropolone-related natural compound that can induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


