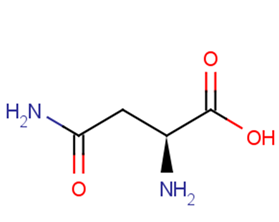
L-Asparagine
CAS No. 70-47-3
L-Asparagine( Asparagine | Altheine | Agedoite | L-Asparagine | NSC 82391 )
Catalog No. M19019 CAS No. 70-47-3
L-asparagine is a non-essential amino acid that is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Asparagine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-asparagine is a non-essential amino acid that is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue.
-
DescriptionAsparagine is a non-essential amino acid that is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue. It is biosynthesized from ASPARTIC ACID and AMMONIA by asparagine synthetase.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAsparagine | Altheine | Agedoite | L-Asparagine | NSC 82391
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number70-47-3
-
Formula Weight132.11
-
Molecular FormulaC4H8N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O : 6.67 mg/mL 50.48 mM
-
SMILESC(C(C(=O)O)N)C(=O)N
-
Chemical NameL-asparagine
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
InhA-IN-4
InhA-IN-4 (TU14) is a potent inhibitor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis InhA (enoyl ACP reductase), with potential anticancer and antiproliferative activities for studying Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.
-
CysHHC10
CysHHC10 is a synthetic antimicrobial peptide (AMP), and exhibits strong anti-microbial properties against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
-
Cetalkonium chloride
Cetalkonium chloride(Benzylcetyldimethylammonium chloride hydrate) is an ammonium preservative with anti-inflammatory activity that can be used in the study of aphthous ulcers.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


