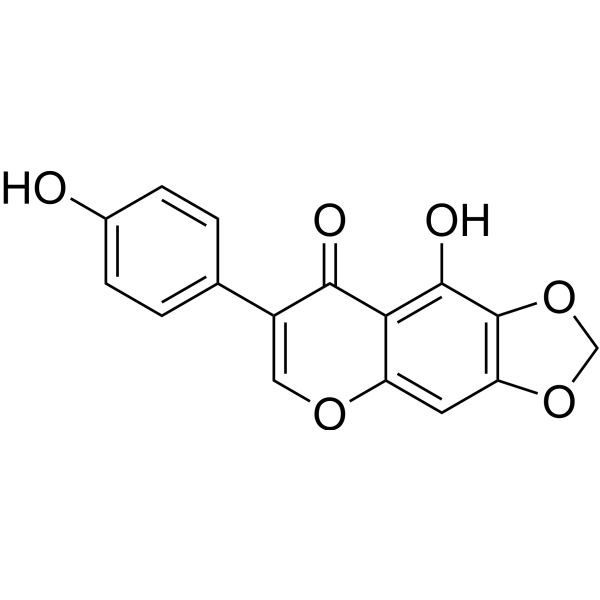
Irilone
CAS No. 41653-81-0
Irilone( —— )
Catalog No. M31824 CAS No. 41653-81-0
Irilone has immunomodulatory, and α-amylase inhibitory activities, it exhibits the selective inhibition toward CYP3 A4 rather than other major human CYPs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 610 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIrilone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIrilone has immunomodulatory, and α-amylase inhibitory activities, it exhibits the selective inhibition toward CYP3 A4 rather than other major human CYPs.
-
DescriptionIrilone has immunomodulatory, and α-amylase inhibitory activities, it exhibits the selective inhibition toward CYP3 A4 rather than other major human CYPs. Irilone exhibited prominent antioxidant activities with the IC50 value of 10.46μM. Irilone potentiated the effect of progesterone in both endometrial and ovarian cancer cell lines, it protected dopaminergic neurons against LPS-induced injury through inhibition of microglia activation and proinflammatory factors generation.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number41653-81-0
-
Formula Weight298.25
-
Molecular FormulaC16H10O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
REBAUDIOSIDE B(P)(NE...
REBAUDIOSIDE B tastes about 150 times sweeter than sucrose and it is non-caloric.
-
Cystathionine-γ-lyas...
Cystathionine-γ-lyase-IN-1 (SHIP-2a) is a selective inhibitor of cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) enzyme (IC50= 6.3 μM).
-
5-Deoxystrigol
5-Deoxystrigol is a highly active Striga germination stimulant.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


