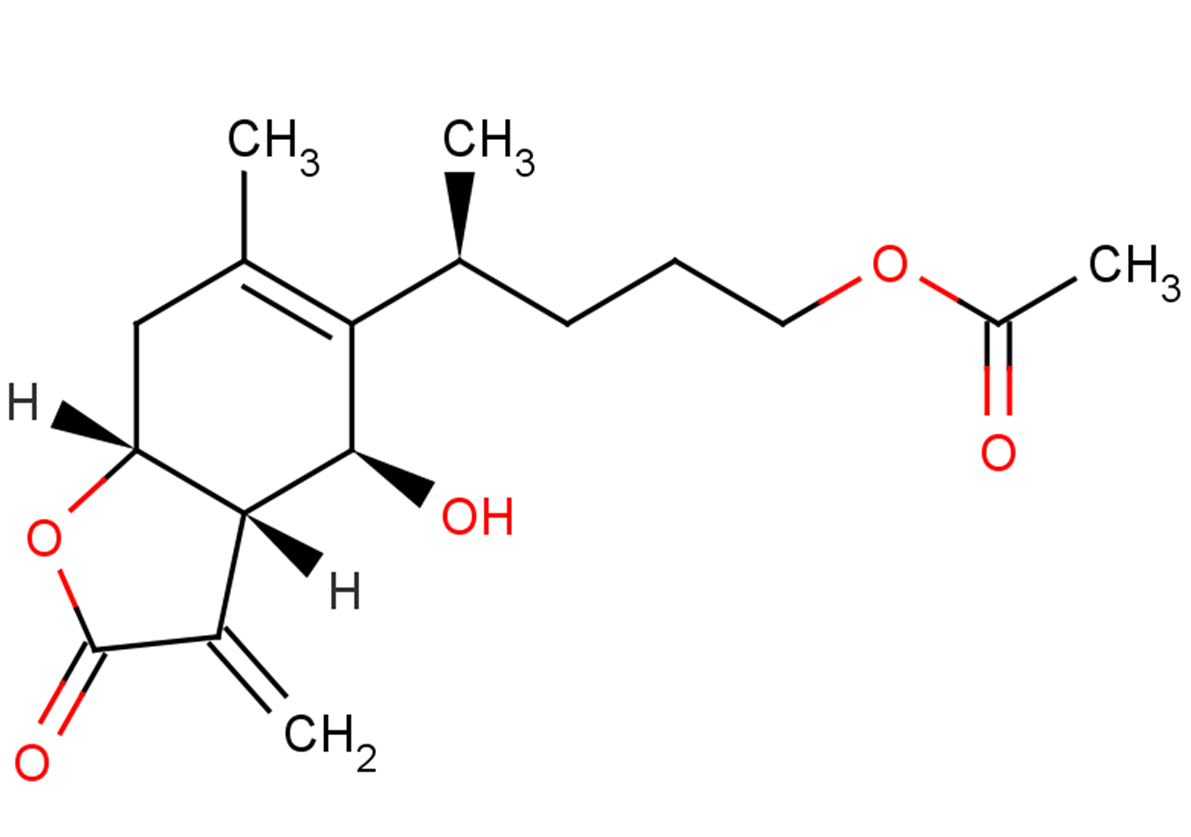
Inulicin
CAS No. 33627-41-7
Inulicin( 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone )
Catalog No. M24280 CAS No. 33627-41-7
Inulicin, an active compound isolated from Inula Britannica L, inhibits VEGF-mediated activation of Src and FAK.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 147 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 225 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 376 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 561 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 798 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameInulicin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionInulicin, an active compound isolated from Inula Britannica L, inhibits VEGF-mediated activation of Src and FAK.
-
DescriptionInulicin, an active compound isolated from Inula Britannica L, inhibits VEGF-mediated activation of Src and FAK.
-
In VitroInulicin (1-O-Acetylbritannilactone) inhibits angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth through regulating VEGF-Src-FAK signaling. Inulicin dose-dependently inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced proliferation, migration, and capillary structure formation of cultured human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment of A549 NSCLC cells with Inulicin results in cell growth inhibition and Src-FAK in-activation. The potential effect of Inulicin is tested ton Src and FAK phosphorylation in A549 lung cancer cells. Significant high levels of Src and FAK phosphorylations are noticed a in A549 cells, which are both inhibited by treatment of Inulicin (5 μM and 10 μM). Src and FAK are both important for cancer cell proliferation. Thus, A549 cell growth, tested by MTT assay and clonogenicity assay,is remarkably inhibited by corresponding Inulicin treatment. The anti-A549 cell growth activity of Inulicin is again dose-dependent. Inulicin (1-O-Acetylbritannilactone) isolated from Inula britannica-F., inhibits inflammatory responses in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Inulicin (5, 10, 20 μM) has several concentration dependent effects, including inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced PGE2 production and COX-2 expression, and blockade of NF-κB activation and translocation. In addition, Inulicin directly inhibits the binding of active NF-κB to specific DNA cis-element.
-
In VivoAdministration of a single dose of Inulicin (1-O-Acetylbritannilactone; 12 mg/kg/day) remarkably suppresses growth of A549 xenografts in nude mice. In vivo microvessels formation and Src activation are also significantly inhibited in Inulicin-treated xenograft tumors. To investigate the potential activity of Inulicin in vivo, a nude mice xenograft model is applied. A single dose of Inulicin (12 mg/kg/day, i.p.) dramatically inhibits the growth of A549 xenografts in nude mice. Further, the weights of Inulicin-treated tumors are remarkably lighter than that of vehicle-treated tumors. Notably, Inulicin administration does not affect mice body weights.
-
Synonyms1-O-Acetylbritannilactone
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetCOX
-
RecptorCOX-2|FAK|NF-κB|Src
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number33627-41-7
-
Formula Weight308.37
-
Molecular FormulaC17H24O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol:45 mg/mL (145.93 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESO[C@H]1[C@@](C2=C)([H])[C@@](OC2=O)([H])CC(C)=C1[C@@H](C)CCCOC(C)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zhengfu H, et al. 1-o-acetylbritannilactone (ABL) inhibits angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth through regulating VEGF-Src-FAK signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 21;464(2):422-7.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Inulicin
Inulicin, an active compound isolated from Inula Britannica L, inhibits VEGF-mediated activation of Src and FAK.
-
Meclofenamate Sodium
A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent with antipyretic and antigranulation activities. It also inhibits prostaglandin biosynthesis.
-
Firocoxib
Firocoxib is a selective non-steroidal inhibitor of cycooxygenase-2 (COX-2) (IC50 of 0.13 μM), with anti-inflammatory for use in dogs and horses.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


