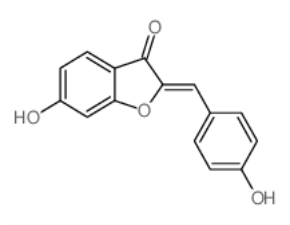
Hispidol
CAS No. 5786-54-9
Hispidol( (Z)-Hispidol )
Catalog No. M17546 CAS No. 5786-54-9
Hispidol ((Z)-Hispidol) is a potential therapeutic for inflammatory bowel disease; inhibits TNF-α induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells with an IC50 of 0.50 μM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 80 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 132 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 201 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 260 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 410 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 560 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 954 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHispidol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHispidol ((Z)-Hispidol) is a potential therapeutic for inflammatory bowel disease; inhibits TNF-α induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells with an IC50 of 0.50 μM.
-
DescriptionHispidol ((Z)-Hispidol) is a potential therapeutic for inflammatory bowel disease; inhibits TNF-α induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells with an IC50 of 0.50 μM.
-
In VitroHispidol shows potent inhibitory effect (>70%) on the TNF-α-induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells, which is one of the hallmark events leading to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Hispidol shows strong inhibitory activities against TNF-α-induced monocytic-colonic epithelial cell adhesion as well as LPS-induced TNF-α expression, is as an excellent candidate for IBD drug development. This inhibition of TNF-α expression by hispidol corresponds to the additional inhibitory activity against AP-1 transcriptional activity, which is another transcription factor required for high level TNF-α expression.
-
In VivoThe oral administration of hispidol suppresses significantly and dose-dependently TNBS-induced rat colitis. Oral administration of hispidol suppresses TNBS-induced colitis in a dose-dependent manner. There is a significant recovery in body weight decrease and colon tissue edematous inflammation. A higher dose (30 mg/kg) of hispidol shows a similar recovery effect to that of 300 mg/kg sulfasalazine. In the colon tissues, TNBS induces a dramatic increase in the level of MPO, a biochemical marker of inflammation, which is suppressed significantly by hispidol in a dose-dependent manner.
-
Synonyms(Z)-Hispidol
-
PathwayJAK/STAT Signaling
-
TargetSTAT
-
RecptorTNF-α
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number5786-54-9
-
Formula Weight254.24
-
Molecular FormulaC15H10O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL; 393.33 mM
-
SMILESc1cc(ccc1/C=C\1/C(=O)c2c(O1)cc(cc2)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kadayat TM, et al. Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 8;137:575-597.
molnova catalog



related products
-
ML115
ML115 is a potent and selective activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), with abn EC50 of 2.0 nM, and is inactive against the related STAT1 and NFκB anti-targets.
-
RSVA 405
RSVA 405 is an AMPK activator (EC50 = 1 μM), and is STAT3 inhibitor.
-
GTS 21 dihydrochlori...
GTS 21 dihydrochloride is a nAChRs agonist. nAChRs are neuron receptor proteins that activated by the binding of the neurotransmitter ACh.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


