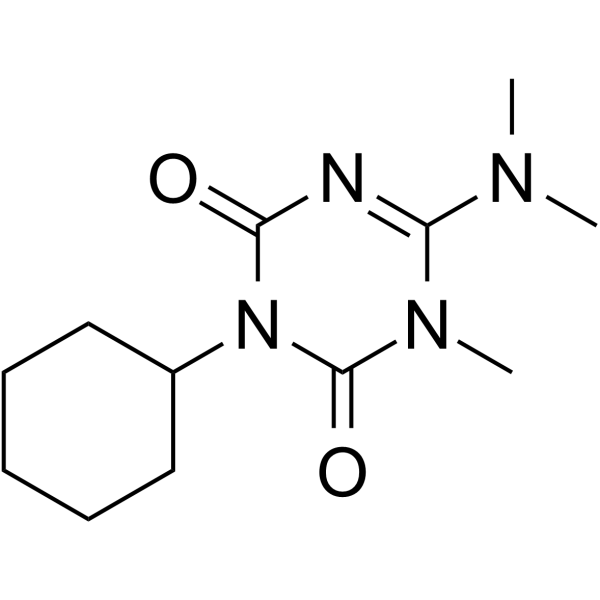
Hexazinone
CAS No. 51235-04-2
Hexazinone( —— )
Catalog No. M27352 CAS No. 51235-04-2
Hexazinone is a broad-spectrum herbicide from the triazine family. Hexazinone inhibits photosynthesis through binding to the D-1 quinone protein of the electron transport chain in photosystem II.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 63 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 103 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 150 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 223 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 482 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHexazinone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHexazinone is a broad-spectrum herbicide from the triazine family. Hexazinone inhibits photosynthesis through binding to the D-1 quinone protein of the electron transport chain in photosystem II.
-
DescriptionHexazinone is a broad-spectrum herbicide from the triazine family. Hexazinone inhibits photosynthesis through binding to the D-1 quinone protein of the electron transport chain in photosystem II.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorLSD1|MAO-A|MAO-B
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number51235-04-2
-
Formula Weight252.318
-
Molecular FormulaC12H20N4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCN(C)c1nc(=O)n(C2CCCCC2)c(=O)n1C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Shuaiying Cui, et al. The LSD1 inhibitor RN-1 induces fetal hemoglobin synthesis and reduces disease pathology in sickle cell mice. Blood. 2015 Jul 16;126(3):386-96.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Propionylcarnitine
Propionylcarnitine (Propionyl carnitine) is a widely used dietary supplement that has been associated with glaucoma and does it ruptu
-
Herbacetin 3-sophoro...
The herbs of Rhodiola rosea.
-
Inaxaplin
Inaxaplin is an apolipoprotein L1 ( APOL1 ) function inhibitor (WO2020131807, compound 2). Inaxaplin can be used for the research of kidney disease.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


